Effects of Dl-3-n-butylphthalide on cognitive functions and blood-brain barrier in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats
- PMID: 37243759
- PMCID: PMC10567816
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-023-02530-5
Effects of Dl-3-n-butylphthalide on cognitive functions and blood-brain barrier in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Effects of Dl-3‑n‑butylphthalide on cognitive functions and blood-brain barrier in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;396(11):3337. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02580-9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37347267 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
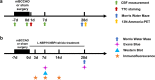
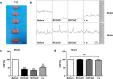
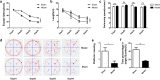
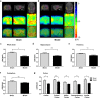
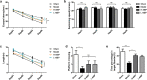
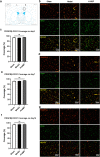
Vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) has been one of the major types of cognitive impairment. Blood-brain barrier damage plays an essential part in the pathogenesis of VCI. At present, the treatment of VCI is mainly focused on prevention, with no drug clinically approved for the treatment of VCI. This study aimed to investigate the effects of DL-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) on VCI rats. A modified bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (mBCCAO) model was applied to mimic VCI. The feasibility of the mBCCAO model was verified by laser Doppler, 13N-Ammonia-Positron Emission Computed Tomography (PET), and Morris Water Maze. Subsequently, the Morris water maze experiment, Evans blue staining, and western blot of tight junction protein were performed to evaluate the effect of different doses of NBP (40 mg/kg, 80 mg/kg) on the improvement of cognitive impairment and BBB disruption induced by mBCCAO. Immunofluorescence was employed to examine the changes in pericyte coverage in the mBCCAO model and the effect of NBP on pericyte coverage was preliminarily explored. mBCCAO surgery led to obvious cognitive impairment and the decrease of whole cerebral blood flow, among which the blood flow in the cortex, hippocampus and thalamus brain regions decreased more significantly. High-dose NBP (80 mg/kg) improved long-term cognitive function in mBCCAO rats, alleviated Evans blue leakage and reduced the loss of tight junction proteins (ZO-1, Claudin-5) in the early course of the disease, thereby exerting a protective effect on the blood-brain barrier. No significant changes in pericyte coverage were observed after mBCCAO. High-dose NBP improved cognitive function in mBCCAO rats. High-dose NBP protected the integrity of BBB by upregulating TJ protein expression, rather than regulating pericyte coverage ratio. NBP could be a potential drug for the treatment of VCI.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; Pericyte; Vascular cognitive impairment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
dl-3-n-butylphthalide preserves white matter integrity and alleviates cognitive impairment in mice with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Sep;25(9):1042-1053. doi: 10.1111/cns.13189. Epub 2019 Jul 23. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 31334611 Free PMC article.
-
DL-3-n-butylphthalide protects the blood-brain barrier against ischemia/hypoxia injury via upregulation of tight junction proteins.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Jun 5;132(11):1344-1353. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000232. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 30939485 Free PMC article.
-
3‑N‑Butyphthalide improves learning and memory in rats with vascular cognitive impairment by activating the SIRT1/BDNF pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Jul;22(1):525-533. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11106. Epub 2020 May 4. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32377741 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of blood brain barrier dysfunction during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in vascular cognitive impairment.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 16;12(4):1639-1658. doi: 10.7150/thno.68304. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35198062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Cognitive Impairment-The Molecular Basis and Potential Influence of the Gut Microbiota on the Pathological Process.Cells. 2024 Nov 27;13(23):1962. doi: 10.3390/cells13231962. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of DL-3-N-butylphthalide in the treatment of ischemic poststroke aphasia: A randomized clinical trial.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Dec;11(12):3300-3309. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52238. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39575649 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide ameliorates diabetic foot ulcer by inhibiting apoptosis and promoting angiogenesis.World J Diabetes. 2025 Apr 15;16(4):101916. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101916. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40236845 Free PMC article.
-
A New Perspective in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke: Ferroptosis.Neurochem Res. 2024 Apr;49(4):815-833. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04096-3. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38170383 Review.
-
Annexin A1 Mitigates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in a Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy Model by Enhancing the Expression of Occludin and Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1).CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Dec;30(12):e70173. doi: 10.1111/cns.70173. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39727329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Che P, Zhang J, Yu M, Tang P, Wang Y, Lin A, et al. Dl-3-n-butylphthalide promotes synaptic plasticity by activating the Akt/ERK signaling pathway and reduces the blood-brain barrier leakage by inhibiting the HIF-1alpha/MMP signaling pathway in vascular dementia model mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(5):1392–1404. doi: 10.1111/cns.14112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duncombe J, Kitamura A, Hase Y, Ihara M, Kalaria RN, Horsburgh K. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a key mechanism leading to vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Closing the translational gap between rodent models and human vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Clin Sci (Lond) 2017;131(19):2451–2468. doi: 10.1042/CS20160727. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

