The research progress of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors from 2020 to 2022
- PMID: 37244162
- PMCID: PMC10201905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115491
The research progress of SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors from 2020 to 2022
Abstract
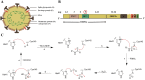
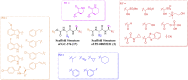
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has spread worldwide. The main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 plays a central role in viral replication and transcription and represents an attractive drug target for fighting COVID-19. Many SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors have been reported, including covalent and noncovalent inhibitors. The SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor PF-07321332 (Nirmatrelvir) designed by Pfizer has been put on the market. This paper briefly introduces the structural characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro and summarizes the research progress of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors from the aspects of drug repurposing and drug design. These information will provide a basis for the drug development of treating the infection of SARS-CoV-2 and even other coronaviruses in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19; Drug design; Drug repurposing; M(pro) inhibitors; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures











References
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xie X., Hu L., Xue H., Xiong Y., Panayi A.C., Lin Z., Chen L., Yan C., Zhou W., Mi B., Liu G. Prognosis and treatment of complications associated with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Materia Medica. 2022;1:124–137.
-
- Chan J.F.W., Yuan S., Kok K.H., To K.K.W., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C.Y., Poon R.W.S., Tsoi H.W., Lo S.K.F., Chan K.H., Poon V.K.M., Chan W.M., Ip J.D., Cai J.P., Cheng V.C.C., Chen H., Hui C.K.M., Yuen K.Y. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

