Is there a role for specialized pro-resolving mediators in pulmonary fibrosis?
- PMID: 37244406
- PMCID: PMC10335230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108460
Is there a role for specialized pro-resolving mediators in pulmonary fibrosis?
Abstract
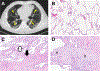
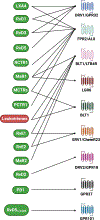
Pulmonary fibrotic diseases are characterized by proliferation of lung fibroblasts and myofibroblasts and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins. Depending on the specific form of lung fibrosis, there can be progressive scarring of the lung, leading in some cases to respiratory failure and/or death. Recent and ongoing research has demonstrated that resolution of inflammation is an active process regulated by families of small bioactive lipid mediators termed "specialized pro-resolving mediators." While there are many reports of beneficial effects of SPMs in animal and cell culture models of acute and chronic inflammatory and immune diseases, there have been fewer reports investigating SPMs and fibrosis, especially pulmonary fibrosis. Here, we will review evidence that resolution pathways are impaired in interstitial lung disease, and that SPMs and other similar bioactive lipid mediators can inhibit fibroblast proliferation, myofibroblast differentiation, and accumulation of excess extracellular matrix in cell culture and animal models of pulmonary fibrosis, and we will consider future therapeutic implications of SPMs in fibrosis.
Keywords: Fibroblast; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Interstitial lung disease; Pro-resolving mediators; SPMs; Sarcoidosis; Scleroderma.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Dr. Sime is a paid consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim, UCB Pharma S.A., and Three Lakes Foundation. She serves on the board for the American Thoracic Society, the scientific council of the Parker Francis Foundation, an advisory board for Galecto, and the medical scientific advisory committee for the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation. She receives grant funding from the NIH. Dr. Sime holds patents related to fibrosis. The other authors have no financial interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Abreu SC, Lopes-Pacheco M, da Silva AL, Xisto DG, de Oliveira TB, Kitoko JZ, de Castro LL, Amorim NR, Martins V, Silva LHA, Goncalves-de-Albuquerque CF, de Castro Faria-Neto HC, Olsen PC, Weiss DJ, Morales MM, Diaz BL, & Rocco PRM (2018). Eicosapentaenoic Acid Enhances the Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in Experimental Allergic Asthma. Front Immunol, 9, 1147. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artiach G, Carracedo M, Claria J, Laguna-Fernandez A, & Back M (2018). Opposing Effects on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Macrophage-induced Inflammation Reveal a Protective Role for the Proresolving Lipid Mediator Receptor ChemR23 in Intimal Hyperplasia. Front Pharmacol, 9, 1327. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

