Proteogenomic Features of the Highly Polymorphic Histidine-rich Glycoprotein Arose Late in Evolution
- PMID: 37244517
- PMCID: PMC10388577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100585
Proteogenomic Features of the Highly Polymorphic Histidine-rich Glycoprotein Arose Late in Evolution
Abstract
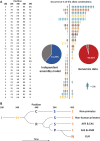
Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) is a liver-produced protein circulating in human serum at high concentrations of around 125 μg/ml. HRG belongs to the family of type-3 cystatins and has been implicated in a plethora of biological processes, albeit that its precise function is still not well understood. Human HRG is a highly polymorphic protein, with at least five variants with minor allele frequencies of more than 10%, variable in populations from different parts of the world. Considering these five mutations we can theoretically expect 35 = 243 possible genetic HRG variants in the population. Here, we purified HRG from serum of 44 individual donors and investigated by proteomics the occurrence of different allotypes, each being either homozygote or heterozygote for each of the five mutation sites. We observed that some mutational combinations in HRG were highly favored, while others were apparently missing, although they ought to be present based on the independent assembly of these five mutation sites. To further explore this behavior, we extracted data from the 1000 genome project (n ∼ 2500 genomes) and assessed the frequency of different HRG mutants in this larger dataset, observing a prevailing agreement with our proteomics data. From all the proteogenomic data we conclude that the five different mutation sites in HRG are not occurring independently, but several mutations at different sites are fully mutually exclusive, whereas others are highly intwined. Specific mutations do also affect HRG glycosylation. As the levels of HRG have been suggested as a protein biomarker in a variety of biological processes (e.g., aging, COVID-19 severity, severity of bacterial infections), we here conclude that the highly polymorphic nature of the protein needs to be considered in such proteomics evaluations, as these mutations may affect HRG's abundance, structure, posttranslational modifications, and function.
Keywords: 1000-genome project; histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG); plasma proteomics; protein biomarker; proteogenomics; serum proteomics.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genotype-dependent N-glycosylation and newly exposed O-glycosylation affect plasmin-induced cleavage of histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG).J Biol Chem. 2024 Mar;300(3):105683. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105683. Epub 2024 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38272220 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein blocks collagen-binding integrins and adhesion of endothelial cells through low-affinity interaction with α2 integrin.Matrix Biol. 2015 Oct;48:89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Matrix Biol. 2015. PMID: 26051322
-
New insights into the functions of histidine-rich glycoprotein.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013;304:467-93. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407696-9.00009-9. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23809442 Review.
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein function in hepatocellular carcinoma depends on its N-glycosylation status, and it regulates cell proliferation by inhibiting Erk1/2 phosphorylation.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):30222-31. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4997. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26336134 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine-rich glycoprotein modulation of immune/autoimmune, vascular, and coagulation systems.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008 Jun;34(3):307-12. doi: 10.1007/s12016-007-8058-6. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18219588 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis for Targeting Hub Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment.Curr Genomics. 2025;26(1):48-80. doi: 10.2174/0113892029308243240709073945. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Curr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39911278 Free PMC article.
-
Multitiered Proteome Analysis Displays the Hyperpermeability of the Rheumatoid Synovial Compartment for Plasma Proteins.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Feb;24(2):100900. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100900. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39746544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poon I.K.H., Patel K.K., Davis D.S., Parish C.R., Hulett M.D. Histidine-rich glycoprotein: the swiss army knife of mammalian plasma. Blood. 2011;117:2093–2101. - PubMed
-
- Lee C., Bongcam-Rudloff E., Sollner C., Jahnen-Dechent W., Claesson-Welsh L. Type 3 cystatins; fetuins, kininogen and histidine-rich glycoprotein. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009;14:2911–2922. - PubMed
-
- Mori S., Takahashi H.K., Yamaoka K., Okamoto M., Nishibori M. High affinity binding of serum histidine-rich glycoprotein to nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid: the application to microquantification. Life Sci. 2003;73:93–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

