Myeloid MyD88 restricts CD8+ T cell response to radiation therapy in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 37244938
- PMCID: PMC10224952
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-35834-w
Myeloid MyD88 restricts CD8+ T cell response to radiation therapy in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
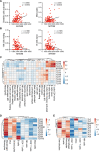
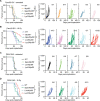
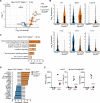
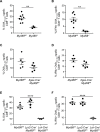
Radiation therapy induces immunogenic cell death in cancer cells, whereby released endogenous adjuvants are sensed by immune cells to direct adaptive immune responses. TLRs expressed on several immune subtypes recognize innate adjuvants to direct downstream inflammatory responses in part via the adapter protein MyD88. We generated Myd88 conditional knockout mice to interrogate its contribution to the immune response to radiation therapy in distinct immune populations in pancreatic cancer. Surprisingly, Myd88 deletion in Itgax (CD11c)-expressing dendritic cells had little discernable effects on response to RT in pancreatic cancer and elicited normal T cell responses using a prime/boost vaccination strategy. Myd88 deletion in Lck-expressing T cells resulted in similar or worsened responses to radiation therapy compared to wild-type mice and lacked antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses from vaccination, similar to observations in Myd88-/- mice. Lyz2-specific loss of Myd88 in myeloid populations rendered tumors more susceptible to radiation therapy and elicited normal CD8+ T cell responses to vaccination. scRNAseq in Lyz2-Cre/Myd88fl/fl mice revealed gene signatures in macrophages and monocytes indicative of enhanced type I and II interferon responses, and improved responses to RT were dependent on CD8+ T cells and IFNAR1. Together, these data implicate MyD88 signaling in myeloid cells as a critical source of immunosuppression that hinders adaptive immune tumor control following radiation therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.G. and M.R.C. received research funding from Bristol Myers-Squibb, Jounce, and VIR Biotech that was unrelated to this manuscript. M.R.C has performed consultancy for Roche. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rotavirus-Induced Expansion of Antigen-Specific CD8 T Cells Does Not Require Signaling via TLR3, MyD88 or the Type I Interferon Receptor.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 7;13:814491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.814491. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464475 Free PMC article.
-
Myd88 Initiates Early Innate Immune Responses and Promotes CD4 T Cells during Coronavirus Encephalomyelitis.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(18):9299-312. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01199-15. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26136579 Free PMC article.
-
MyD88 and interferon-alpha/beta are differentially required for dendritic cell maturation but dispensable for development of protective memory against Listeria.Immunology. 2009 Nov;128(3):429-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03128.x. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 20067542 Free PMC article.
-
MyD88 and TRIF synergistic interaction is required for TH1-cell polarization with a synthetic TLR4 agonist adjuvant.Eur J Immunol. 2013 Sep;43(9):2398-408. doi: 10.1002/eji.201243124. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Eur J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23716300 Free PMC article.
-
A Synthetic CD8α:MyD88 Coreceptor Enhances CD8+ T-cell Responses to Weakly Immunogenic and Lowly Expressed Tumor Antigens.Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 15;77(24):7049-7058. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0653. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29055013 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel small molecule Enpp1 inhibitor improves tumor control following radiation therapy by targeting stromal Enpp1 expression.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 2;14(1):29913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80677-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39622844 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of immunogenic cell death inducers in cancer immunotherapy: turning cold tumors hot.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 7;12:1363121. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1363121. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38774648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated characteristics and immune dysregulation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma under the regulation of m7G-related tumor microenvironment cells.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Jun 25;22(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03441-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38918785 Free PMC article.
-
The immunogenic radiation and new players in immunotherapy and targeted therapy for head and neck cancer.Front Oral Health. 2023 Jul 11;4:1180869. doi: 10.3389/froh.2023.1180869. eCollection 2023. Front Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37496754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

