A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 37246815
- PMCID: PMC10527073
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.29450
A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Background: Rescue of mitochondrial function is a promising neuroprotective strategy for Parkinson's disease (PD). Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has shown considerable promise as a mitochondrial rescue agent across a range of preclinical in vitro and in vivo models of PD.
Objectives: To investigate the safety and tolerability of high-dose UDCA in PD and determine midbrain target engagement.
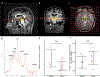
Methods: The UP (UDCA in PD) study was a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of UDCA (30 mg/kg daily, 2:1 randomization UDCA vs. placebo) in 30 participants with PD for 48 weeks. The primary outcome was safety and tolerability. Secondary outcomes included 31-phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31 P-MRS) to explore target engagement of UDCA in PD midbrain and assessment of motor progression, applying both the Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale Part III (MDS-UPDRS-III) and objective, motion sensor-based quantification of gait impairment.
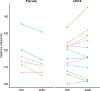
Results: UDCA was safe and well tolerated, and only mild transient gastrointestinal adverse events were more frequent in the UDCA treatment group. Midbrain 31 P-MRS demonstrated an increase in both Gibbs free energy and inorganic phosphate levels in the UDCA treatment group compared to placebo, reflecting improved ATP hydrolysis. Sensor-based gait analysis indicated a possible improvement of cadence (steps per minute) and other gait parameters in the UDCA group compared to placebo. In contrast, subjective assessment applying the MDS-UPDRS-III failed to detect a difference between treatment groups.
Conclusions: High-dose UDCA is safe and well tolerated in early PD. Larger trials are needed to further evaluate the disease-modifying effect of UDCA in PD. © 2023 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: 31P-MR spectroscopy; UDCA; neuroprotection; supervised gait analysis; ursodeoxycholic acid.
© 2023 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 1990;54(3):823–7. - PubMed
-
- Zambrano K, Barba D, Castillo K, et al. Fighting Parkinson’s disease: The return of the mitochondria. Mitochondrion. 2022;64:34–44. - PubMed
-
- Schapira AH, Olanow CW, Greenamyre JT, Bezard E. Slowing of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease: future therapeutic perspectives. Lancet. 2014;384(9942):545–55. - PubMed
-
- Mortiboys H, Aasly J, Bandmann O. Ursocholanic acid rescues mitochondrial function in common forms of familial Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 10):3038–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

