G Protein-Coupled Receptor 75 (GPR75) As a Novel Molecule for Targeted Therapy of Cancer and Metabolic Syndrome
- PMID: 37247305
- PMCID: PMC10495892
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.5.1817
G Protein-Coupled Receptor 75 (GPR75) As a Novel Molecule for Targeted Therapy of Cancer and Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
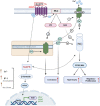
In recent years, molecular targeted therapy has attracted more attention from researchers due to its high efficiency and fewer side effects. Researchers are attempting to find more specific ways to treat diseases. It has been found that there are different targets for the treatment of diseases such as cancer, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. It is important to find a potential target in order to lessen the side effects of current treatments. G Protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large family of transmembrane proteins that are expressed in many organs, leading to the activation of internal signal transduction cascades through the binding of different ligands, including neurotransmitters, peptides, and lipids. Due to the critical role of GPCRs in cells, it could be a potential target. G protein-coupled receptor 75 (GPR75) is a novel member of the GPCR family that has an important role in many diseases, such as obesity, cancer, and metabolic syndrome. Until now, three ligands have been detected for GPR75, including 20-HETE, CCL5, and RANTES. Recent studies suggest that 20-HETE, through GPR75, triggers signaling pathways including PI3K/Akt and RAS/MAPK, leading to a more aggressive phenotype in prostate cancer cells. Additionally, the PI3K/Akt and RAS/MAPK signaling pathways activate NF-κB, which is significant in various pathways of cancer development such as proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. The findings indicate that inhibiting GPR75 in humans leads to an increase in insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, as well as a reduction in body fat storage. According to these discoveries, GPR75 could be a potential target for drug treatment of diseases such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. In this review, we aimed to discuss the therapeutic impact of GPR75 in cancer, metabolic syndrome, and obesity and underscore the possible pathways.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptors 75; Metabolic Syndrome; Molecular Targeted Therapy; Obesity; cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential competing interest was reported by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GPR75: Advances, Challenges in Deorphanization, and Potential as a Novel Drug Target for Disease Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4084. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094084. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GPR75: An exciting new target in metabolic syndrome and related disorders.Biochimie. 2022 Apr;195:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2022.01.005. Epub 2022 Jan 16. Biochimie. 2022. PMID: 35045335 Review.
-
RANTES stimulates Ca2+ mobilization and inositol trisphosphate (IP3) formation in cells transfected with G protein-coupled receptor 75.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;149(5):490-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706909. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17001303 Free PMC article.
-
GPR75 receptor mediates 20-HETE-signaling and metastatic features of androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Feb;1865(2):158573. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158573. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 31760076 Free PMC article.
-
20-HETE Signals Through G-Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR75 (Gq) to Affect Vascular Function and Trigger Hypertension.Circ Res. 2017 May 26;120(11):1776-1788. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310525. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28325781 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CYP1A1/20-HETE/GPR75 Axis-Mediated Arachidonic Acid Metabolism Dysregulation in H-Type Hypertension Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5947. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135947. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649725 Free PMC article.
-
GPR75: A Newly Identified Receptor for Targeted Intervention in the Treatment of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome.Cardiol Rev. 2024 May 2:10.1097/CRD.0000000000000711. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000711. Online ahead of print. Cardiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38695569
-
Co-delivery of artemisinin and metformin via PEGylated niosomal nanoparticles: potential anti-cancer effect in treatment of lung cancer cells.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):133-144. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00495-7. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Daru. 2024. PMID: 38168007 Free PMC article.
-
Effect and mechanism of GPR75 in metabolic dysfunction-related steatosis liver disease.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Sep 9;21(12):2343-2347. doi: 10.7150/ijms.101094. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39310267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CYP4/20-HETE/GPR75 axis in the progression metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease (MASLD) to chronic liver disease.Front Physiol. 2025 Jan 29;15:1497297. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1497297. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39959811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A Tanagho P, S Shohdy K. GPR 120: the potential target for obesity treatment. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2016;16:8–11. - PubMed
-
- Alagheband Y, Jafari-gharabaghlou D, Imani M, et al. Design and fabrication of a dual-drug loaded nano-platform for synergistic anticancer and cytotoxicity effects on the expression of leptin in lung cancer treatment. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2022;73:103389.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

