From Paper Files to Web-Based Application for Data-Driven Monitoring of HIV Programs: Nigeria's Journey to a National Data Repository for Decision-Making and Patient Care
- PMID: 37247622
- PMCID: PMC10462428
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1768711
From Paper Files to Web-Based Application for Data-Driven Monitoring of HIV Programs: Nigeria's Journey to a National Data Repository for Decision-Making and Patient Care
Abstract
Background: Timely and reliable data are crucial for clinical, epidemiologic, and program management decision making. Electronic health information systems provide platforms for managing large longitudinal patient records. Nigeria implemented the National Data Repository (NDR) to create a central data warehouse of all people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLHIV) while providing useful functionalities to aid decision making at different levels of program implementation.
Objective: We describe the Nigeria NDR and its development process, including its use for surveillance, research, and national HIV program monitoring toward achieving HIV epidemic control.
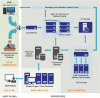
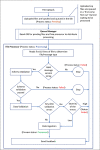
Methods: Stakeholder engagement meetings were held in 2013 to gather information on data elements and vocabulary standards for reporting patient-level information, technical infrastructure, human capacity requirements, and information flow. Findings from these meetings guided the development of the NDR. An implementation guide provided common terminologies and data reporting structures for data exchange between the NDR and the electronic medical record (EMR) systems. Data from the EMR were encoded in extensible markup language and sent to the NDR over secure hypertext transfer protocol after going through a series of validation processes.
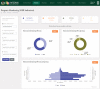
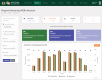
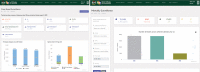
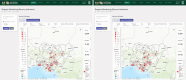
Results: By June 30, 2021, the NDR had up-to-date records of 1,477,064 (94.4%) patients receiving HIV treatment across 1,985 health facilities, of which 1,266,512 (85.7%) patient records had fingerprint template data to support unique patient identification and record linkage to prevent registration of the same patient under different identities. Data from the NDR was used to support HIV program monitoring, case-based surveillance and production of products like the monthly lists of patients who have treatment interruptions and dashboards for monitoring HIV test and start.
Conclusion: The NDR enabled the availability of reliable and timely data for surveillance, research, and HIV program monitoring to guide program improvements to accelerate progress toward epidemic control.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of interruptions in antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV in Nigeria: a retrospective cohort study using the Nigeria national data repository.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 20;20(3):e0300937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300937. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40112252 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with an interruption in treatment of people living with HIV in USAID-supported states in Nigeria: a retrospective study from 2000-2020.BMC Public Health. 2021 Nov 30;21(1):2194. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-12264-9. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34847909 Free PMC article.
-
Scale-up of networked HIV treatment in Nigeria: creation of an integrated electronic medical records system.Int J Med Inform. 2015 Jan;84(1):58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2014.09.006. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Int J Med Inform. 2015. PMID: 25301692
-
Development and Implementation of the DHAPP Military eHealth Information Network System.Curr HIV Res. 2017;15(2):102-108. doi: 10.2174/1570162X15666170517093714. Curr HIV Res. 2017. PMID: 28521714 Review.
-
Haiti’s National HIV Quality Management Program and the Implementation of an Electronic Medical Record to Drive Improvement in Patient Care.2020 May 27. In: Marquez LR, editor. Improving Health Care in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Case Book [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2020. Chapter 4. 2020 May 27. In: Marquez LR, editor. Improving Health Care in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Case Book [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2020. Chapter 4. PMID: 33347256 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Modernizing Public Health Data Systems and Workforce Capacity: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Public Health Informatics Fellowship Program.J Public Health Manag Pract. 2025 Mar-Apr 01;31(2):263-269. doi: 10.1097/PHH.0000000000002048. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2025. PMID: 39321350 Free PMC article.
-
Piloting the Inclusion of the Key Populations Unique Identifier Code in the South African Routine Health Information Management System: Protocol for a Multiphased Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Sep 6;13:e55092. doi: 10.2196/55092. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39240683 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of interruptions in antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV in Nigeria: a retrospective cohort study using the Nigeria national data repository.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 20;20(3):e0300937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300937. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40112252 Free PMC article.
-
Ensuring equitable access to quality HIV care for affected populations in complex sociocultural settings: Lessons from Nigeria.PLoS One. 2025 May 14;20(5):e0319807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319807. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40367072 Free PMC article.
-
Data Interoperability in Context: The Importance of Open-Source Implementations When Choosing Open Standards.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Apr 15;27:e66616. doi: 10.2196/66616. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40232773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS Global HIV Statistics 2020. End AIDS epidemicAccessed April 18, 2023 at:https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet
-
- UNAIDS 90–90–90 An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic 2014:40. Accessed April 18, 2023 at:https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/90-90-90_en.pdf
-
- UNAIDS Understanding Fast-Track Targets. Accelerating action to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030UNAIDS; 2015. Accessed April 18, 2023 at:https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/201506_JC2743_Und...
-
- Health FMo Nigeria HIV/AIDS Indicator and Impact Survey (NAIIS) 2018: Technical Report; 2019
-
- UNAIDS Country factsheets Nigeria / 2019 HIV and AIDS Estimates Adults and children living with HIVUNAIDS. Updated2019

