Human microglia show unique transcriptional changes in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37248328
- PMCID: PMC10353942
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-023-00424-y
Human microglia show unique transcriptional changes in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
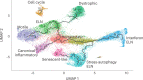
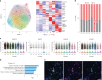
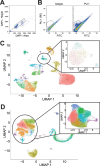
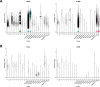
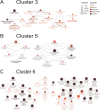
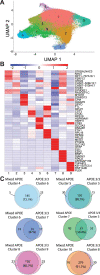
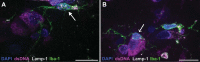
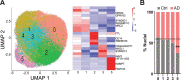
Microglia, the innate immune cells of the brain, influence Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression and are potential therapeutic targets. However, microglia exhibit diverse functions, the regulation of which is not fully understood, complicating therapeutics development. To better define the transcriptomic phenotypes and gene regulatory networks associated with AD, we enriched for microglia nuclei from 12 AD and 10 control human dorsolateral prefrontal cortices (7 males and 15 females, all aged >60 years) before single-nucleus RNA sequencing. Here we describe both established and previously unrecognized microglial molecular phenotypes, the inferred gene networks driving observed transcriptomic change, and apply trajectory analysis to reveal the putative relationships between microglial phenotypes. We identify microglial phenotypes more prevalent in AD cases compared with controls. Further, we describe the heterogeneity in microglia subclusters expressing homeostatic markers. Our study demonstrates that deep profiling of microglia in human AD brain can provide insight into microglial transcriptional changes associated with AD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Comment in
-
Microglial transcriptional changes in AD.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Jul;19(7):387. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00835-w. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37280291 No abstract available.
References
-
- Calsolaro V, Edison P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12:719–732. - PubMed
-
- Milner MT, Maddugoda M, Gotz J, Burgener SS, Schroder K. The NLRP3 inflammasome triggers sterile neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021;68:116–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

