Immunogenicity and safety of COVID-19 BNT162b2 booster vaccine in end-stage kidney disease patients receiving haemodialysis in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: a cohort prospective study
- PMID: 37248445
- PMCID: PMC10226875
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-023-03218-x
Immunogenicity and safety of COVID-19 BNT162b2 booster vaccine in end-stage kidney disease patients receiving haemodialysis in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: a cohort prospective study
Abstract
Background: A significant decrease in antibody titres several months after COVID-19 primary vaccination in end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients receiving maintenance haemodialysis has recently been reported. The waning in antibody titres has led to the recommendations for a booster dose to increase the antibody titres after vaccination. Consequently, it is crucial to analyse the long-term humoral immune responses after COVID-19 primary vaccination and assess the immunogenicity and safety of booster doses in haemodialysis (HD) patients.
Methods: Patients on maintenance haemodialysis who received the primary vaccine of CoronaVac (Sinovac) vaccine were administered with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) as the booster dose. The immunogenicity was assessed before (V1), one month (V2) and eight months (V3) after the primary vaccination, as well as one month after the booster dose (V4). Patients were followed up one month after the booster dose to assess the adverse events (AEs).
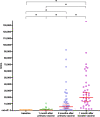
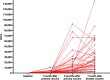
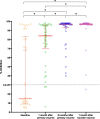
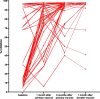
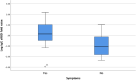
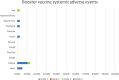
Results: The geometric mean titre (GMT) of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG antibody at 8 months after the primary vaccination increased significantly to 5,296.63 (95%CI: 2,930.89-9,571.94) U/mL (p = < 0.0001) compared to before the primary vaccination. The GMT also increased significantly to 19,142.56 (95% CI: 13,489.63-27,227.01) U/mL (p < 0.0001) 1 month after the booster vaccine. Meanwhile, the median inhibition rate of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) at 8 months after the primary vaccine and 1 month after the booster dose were not significantly different (p > 0.9999). The most common AEs after the booster dose included mild pain at the injection site (55.26%), mild fatigue (10.53%), and swelling at the injection site (10.53%). No serious AEs were reported.
Conclusions: The majority of ESKD patients on haemodialysis mounted a good antibody response to the BNT162b2 booster vaccination with tolerable adverse events.
Keywords: Booster; COVID-19 vaccines; End-stage renal disease; Haemodialysis; Immunogenicity; Safety.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- UK Kidney Association. Covid-19 vaccination for adult patients with kidney disease: a position statement from the UK renal community. UK Kidney Association. 2020. https://ukkidney.org/health-professionals/covid-19/ukka-resources/covid-.... Accessed 2 Dec 2022.
-
- Puspitasari M, Sattwika PD, Rahari DS, Wijaya W, Hidayat ARP, Kertia N, et al. Outcomes of vaccinations against respiratory diseases in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2023;18:e0281160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281160. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohith S, Chandrashekhar H. Breakthrough covid 19 infections after 2 doses of covid 19 vaccination and comparing severity between hospitalized and non hospitalized in tertiary care hospital. J Assoc Physicians India. 2022;70:11–12.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

