Management of regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy: guideline recommendations from Chinese emergency medical doctor consensus
- PMID: 37248514
- PMCID: PMC10226261
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-023-00457-9
Management of regional citrate anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy: guideline recommendations from Chinese emergency medical doctor consensus
Abstract
Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) is widely used for treating critically-ill patients in the emergency department in China. Anticoagulant therapy is needed to prevent clotting in the extracorporeal circulation during CRRT. Regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) has been shown to potentially be safer and more effective and is now recommended as the preferred anticoagulant method for CRRT. However, there is still a lack of unified standards for RCA management in the world, and there are many problems in using this method in clinical practice. The Emergency Medical Doctor Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association (CMDA) organized a panel of domestic emergency medicine experts and international experts of CRRT to discuss RCA-related issues, including the advantages and disadvantages of RCA in CRRT anticoagulation, the principle of RCA, parameter settings for RCA, monitoring of RCA (mainly metabolic acid-base disorders), and special issues during RCA. Based on the latest available research evidence as well as the paneled experts' clinical experience, considering the generalizability, suitability, and potential resource utilization, while also balancing clinical advantages and disadvantages, a total of 16 guideline recommendations were formed from the experts' consensus.
Keywords: Anticoagulation; Citrate; Continuous renal replacement therapy; Emergency; Expert consensus; Guideline.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


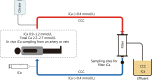
References
-
- Liu C, Mao Z, Kang H, Hu J, Zhou F. Regional citrate versus heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1299-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schilder L, Nurmohamed SA, Bosch FH, Purmer IM, den Boer SS, Kleppe CG, et al. Citrate anticoagulation versus systemic heparinisation in continuous venovenous hemofiltration in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a multi-center randomized clinical trial. Crit Care. 2014;18(4):472. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0472-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kośka A, Kirwan CJ, Kowalik MM, Lango-Maziarz A, Szymanowicz W, Jagielak D, et al. Filter life span in postoperative cardiovascular surgery patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy, using a postdilution regional citrate anticoagulation continuous hemofiltration circuit. Cardiol J. 2022;29(1):53–61. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0039. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

