High-titer convalescent plasma plus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment for non-resolving COVID-19 in six immunocompromised patients
- PMID: 37248664
- PMCID: PMC10320105
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkad144
High-titer convalescent plasma plus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment for non-resolving COVID-19 in six immunocompromised patients
Abstract
Objectives: Immunocompromised patients have an increased risk of severe or prolonged COVID-19. Currently available drugs are registered to treat COVID-19 during the first 5 to 7 days after symptom onset. Data on the effectivity in immunocompromised patients with chronic non-resolving COVID-19 are urgently needed. Here, we report the outcome of patients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir together with high-titer convalescent plasma (CP) in six immunocompromised patients with non-resolving COVID-19.
Methods: Immunocompromised patients with persisting COVID-19 (positive PCR with Ct values <30 for ≥20 days) received off-label therapy with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. It was combined with CP containing BA.5 neutralizing titers of ≥1/640 whenever available. Follow-up was done by PCR and sequencing on nasopharyngeal swabs on a weekly basis until viral genome was undetectable consecutively.
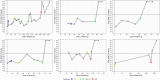
Results: Five immunocompromised patients were treated with high-titer CP and 5 days of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. One patient received nirmatrelvir/ritonavir monotherapy. Median duration of SARS-CoV-2 PCR positivity was 70 (range 20-231) days before nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment. In four patients receiving combination therapy, no viral genome of SARS-CoV-2 was detected on day 7 and 14 after treatment while the patient receiving nirmatrelvir/ritonavir monotherapy, the day 7 Ct value increased to 34 and viral genome was undetectable thereafter. Treatment was unsuccessful in one patient. In this patient, sequencing after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment did not show protease gene mutations.
Conclusions: In immunocompromised patients with non-resolving COVID-19, the combination of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and CP may be an effective treatment. Larger prospective studies are needed to confirm these preliminary results and should compare different treatment durations.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Bas Oude Munnink has received funding by EU Horizon 2020 projects RECoVer (grant number: 101003589) and VEO (grant number: 874735). All other authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Successful treatment of persisting SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient with repeated nirmatrelvir/ritonavir courses: a case report.Infect Dis (Lond). 2023 Aug;55(8):585-589. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2023.2223274. Epub 2023 Jun 18. Infect Dis (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37334428
-
Early combination of sotrovimab with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir or remdesivir is associated with low rate of persisting SARS CoV-2 infection in immunocompromised outpatients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a prospective single-centre study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2439541. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2439541. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39661366 Free PMC article.
-
Association of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir with post-acute sequelae and mortality among patients who are immunocompromised with COVID-19 in Hong Kong: a retrospective cohort study.Lancet Rheumatol. 2025 Feb;7(2):e108-e117. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00224-8. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39527967
-
Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir: First Approval.Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(5):585-591. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01692-5. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35305258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Saving lives with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir one transplant patient at a time".Transpl Infect Dis. 2023 Apr;25(2):e14037. doi: 10.1111/tid.14037. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Transpl Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36847419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early combined therapy for COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients: a promising approach against viral persistence and drug resistance.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 28;25(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11012-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40295963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: An Update on Epidemiology, Prevention and Treatment, September-2023.Infect Dis Clin Microbiol. 2023 Sep 30;5(3):165-187. doi: 10.36519/idcm.2023.251. eCollection 2023 Sep. Infect Dis Clin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38633552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The consequences of SARS-CoV-2 within-host persistence.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2025 May;23(5):288-302. doi: 10.1038/s41579-024-01125-y. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39587352 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of antiviral therapies for the treatment of persistent COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients since the Omicron surge: a systematic review.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 Mar 3;80(3):633-644. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae482. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39804238 Free PMC article.
-
A Multinational Case Series Describing Successful Treatment of Persistent Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection Caused by Omicron Sublineages With Prolonged Courses of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023 Dec 7;11(1):ofad612. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad612. eCollection 2024 Jan. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 38269048 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

