High-titer convalescent plasma plus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment for non-resolving COVID-19 in six immunocompromised patients
- PMID: 37248664
- PMCID: PMC10320105
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkad144
High-titer convalescent plasma plus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment for non-resolving COVID-19 in six immunocompromised patients
Abstract
Objectives: Immunocompromised patients have an increased risk of severe or prolonged COVID-19. Currently available drugs are registered to treat COVID-19 during the first 5 to 7 days after symptom onset. Data on the effectivity in immunocompromised patients with chronic non-resolving COVID-19 are urgently needed. Here, we report the outcome of patients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir together with high-titer convalescent plasma (CP) in six immunocompromised patients with non-resolving COVID-19.
Methods: Immunocompromised patients with persisting COVID-19 (positive PCR with Ct values <30 for ≥20 days) received off-label therapy with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. It was combined with CP containing BA.5 neutralizing titers of ≥1/640 whenever available. Follow-up was done by PCR and sequencing on nasopharyngeal swabs on a weekly basis until viral genome was undetectable consecutively.
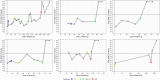
Results: Five immunocompromised patients were treated with high-titer CP and 5 days of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. One patient received nirmatrelvir/ritonavir monotherapy. Median duration of SARS-CoV-2 PCR positivity was 70 (range 20-231) days before nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment. In four patients receiving combination therapy, no viral genome of SARS-CoV-2 was detected on day 7 and 14 after treatment while the patient receiving nirmatrelvir/ritonavir monotherapy, the day 7 Ct value increased to 34 and viral genome was undetectable thereafter. Treatment was unsuccessful in one patient. In this patient, sequencing after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment did not show protease gene mutations.
Conclusions: In immunocompromised patients with non-resolving COVID-19, the combination of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and CP may be an effective treatment. Larger prospective studies are needed to confirm these preliminary results and should compare different treatment durations.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Bas Oude Munnink has received funding by EU Horizon 2020 projects RECoVer (grant number: 101003589) and VEO (grant number: 874735). All other authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

