Caffeine-induced release of small molecules from DNA nanostructures
- PMID: 37250306
- PMCID: PMC10214285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106564
Caffeine-induced release of small molecules from DNA nanostructures
Abstract
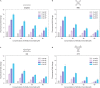
Several planar aromatic molecules are known to intercalate between base pairs of double-stranded DNA. This mode of interaction has been used to stain DNA as well as to load drug molecules onto DNA-based nanostructures. Some small molecules are also known to induce deintercalation in double-stranded DNA, one such molecule being caffeine. Here, we compared the ability of caffeine to cause deintercalation of ethidium bromide, a representative DNA intercalator, from duplex DNA and three DNA motifs of increasing structural complexity (four-way junction, double crossover motif, and DNA tensegrity triangle). We found that caffeine impedes the binding of ethidium bromide in all these structures to the same extent, with some differences in deintercalation profiles. Our results can be useful in the design of DNA nanocarriers for intercalating drugs, where drug release can be chemically stimulated by other small molecules.
Keywords: Chemistry; Molecular self-assembly; Supramolecular chemistry.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.R.C. is a member of the editorial advisory board of iScience.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Quantitative fluorescence method for continuous measurement of DNA hybridization kinetics using a fluorescent intercalator.Anal Biochem. 1995 Jul 1;228(2):208-20. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.1341. Anal Biochem. 1995. PMID: 8572297
-
Intercalators as molecular chaperones in DNA self-assembly.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Jul 31;135(30):11283-8. doi: 10.1021/ja404402b. Epub 2013 Jul 18. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23829631
-
Discriminating small molecule DNA binding modes by single molecule force spectroscopy.FEBS Lett. 2002 Jan 16;510(3):154-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03257-4. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11801245
-
Double-stranded DNA analysis by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence using ethidium bromide as an intercalator.Biotechniques. 1995 Feb;18(2):316-7, 320, 322-3. Biotechniques. 1995. PMID: 7727136
-
Small molecule intercalation with double stranded DNA: implications for normal gene regulation and for predicting the biological efficacy and genotoxicity of drugs and other chemicals.Mutat Res. 2007 Oct 1;623(1-2):53-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2007.03.009. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Mutat Res. 2007. PMID: 17449065 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring caffeine as a disruptor of membrane integrity and genomic stability in Staphylococcus aureus: functional and in silico analysis.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Jan 8;207(2):28. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04230-x. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39779516
-
Fluorometric Determination of DNA Nanostructure Biostability.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 Aug 21;6(8):3074-3078. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00287. Epub 2023 Jun 1. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37262927 Free PMC article.
-
The unusual structural properties and potential biological relevance of switchback DNA.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 12:2023.11.15.563609. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.15.563609. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 6;15(1):6636. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50348-3. PMID: 38014227 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structural DNA nanotechnology at the nexus of next-generation bio-applications: challenges and perspectives.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Dec 19;6(2):386-401. doi: 10.1039/d3na00692a. eCollection 2024 Jan 16. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 38235105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unusual structural properties and potential biological relevance of switchback DNA.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 6;15(1):6636. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50348-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39107287 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

