Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in the Development and Progression of Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 37250384
- PMCID: PMC10224676
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S411168
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in the Development and Progression of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
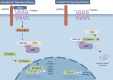
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is a growth control pathway involved in various biological processes as well as the development and progression of cancer. Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies in the world. The hyperactivation of Wnt signaling is observed in almost all CRC and plays a crucial role in cancer-related processes such as cancer stem cell (CSC) propagation, angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), chemoresistance, and metastasis. This review will discuss how the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in the carcinogenesis and progression of CRC and related therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: APC; CRC therapy; Wnt pathway; colorectal carcinogenesis.
© 2023 He and Gan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SDF-1/CXCR4 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of colorectal cancer by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cancer Lett. 2014 Nov 28;354(2):417-26. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.08.012. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25150783
-
RUNX1 promotes tumour metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and EMT in colorectal cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 1;38(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1330-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31370857 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signalling, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and crosslink signalling in colorectal cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jun;175:116685. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116685. Epub 2024 May 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38710151 Review.
-
TRIB3 Interacts With β-Catenin and TCF4 to Increase Stem Cell Features of Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells and Tumorigenesis.Gastroenterology. 2019 Feb;156(3):708-721.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30365932
-
Angiogenesis-Related Functions of Wnt Signaling in Colorectal Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 2;12(12):3601. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123601. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33276489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Cancer Stem Cell Markers in Ovarian Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;16(1):40. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010040. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an in vivo syngeneic mouse transplant model of invasive intestinal adenocarcinoma driven by endogenous expression of Pik3caH1047R and Apc loss.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 2;19(8):e0308051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308051. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39093890 Free PMC article.
-
Nonylphenol promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells by upregulating miR-151a-3p.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 20;16(1):63. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01805-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39832042 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacophore-based identification and in Silico characterization of microbial metabolites as potential modulators of Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer therapy.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb 8. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11103-4. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39921842
-
Utilizing Indigenous Flora in East Africa for Breast Cancer Treatment: An Overview.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(2):99-113. doi: 10.2174/0118715206338557240909081833. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39297456 Review.
References
-
- Nusse R, Varmus HE. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982;31(1):99–109. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985–999. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192–1205. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

