Genetic Polymorphism and serum levels of Insulin like Growth Factor-1 (Igf-1) in patients of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 37250538
- PMCID: PMC10214818
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.39.3.6561
Genetic Polymorphism and serum levels of Insulin like Growth Factor-1 (Igf-1) in patients of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: Insulin like growth factor-1(IGF-1), is a modulator of immunity and inflammation, it promotes the anabolic role of growth hormone (GH) on bone and skeletal tissue. Genetic polymorphism in IGF-1 gene is reported to affect the transcriptional efficiency affecting its serum level. In this study we aim: 1) To study the presence of 192bp polymorphism of IGF-1 gene in patients of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 2) To study the association of 192 bp polymorphism of IGF-1 gene with serum IGF-1 levels and disease severity in patients of RA.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out at University of Health Sciences (UHS), Lahore. Diagnosed RA cases who fulfilled the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria were recruited from Fatima Memorial Hospital (FMH) and Behbud Rheumatology Clinics, Lahore during 2018-2019. Serum IGF-1 levels were determined by ELISA in blood samples of 200 RA patients and 200 healthy individuals. DNA was extracted and genetic polymorphism was determined.
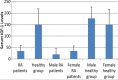
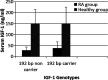
Results: The serum IGF-1 level in RA group was significantly lower compared to healthy group. Our study shows presence of 192bp allele of IGF-1in 77% of the studied population. Carriers of 192bp allele of IGF-1 had a significantly higher serum level of IGF-1 as compared to non-carriers in the RA patients. Rheumatoid factor (RF) positive patients had a higher number of 192bp carriers in comparison to RF negative patients. Significant difference was also seen in severity of disease between carrier and non-carriers of 192bp allele with the disease being more severe in male carriers.
Conclusions: There is an association of IGF-1gene polymorphism with variation in serum IGF-1 levels and severity of RA.
Keywords: Genetic polymorphism; Insulin like growth factor-1; Rheumatoid arthritis; Severity of disease.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 gene polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Scand J Rheumatol. 2012;41(6):421-5. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2012.691177. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Scand J Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22839688
-
Relationship between growth hormone-IGF-I-IGFBP-3 axis and serum leptin levels with bone mass and body composition in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 Jan;44(1):120-5. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh421. Epub 2004 Oct 5. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 15466894
-
Circulating Mir-140 and leptin improve the accuracy of the differential diagnosis between psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study.Transl Res. 2022 Jan;239:18-34. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.08.001. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34380068
-
Low serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 are associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Res. 2019 Sep;69:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 25. Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 31430609
-
Circulating Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-analysis.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(10):1091-1098. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190319124009. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 30892152 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression analysis reveals mir-29 as a linker regulatory molecule among rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and dementia: Insights from systems biology approach.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 15;20(1):e0316584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316584. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39813219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haridoss M, Bagepally BS, Natarajan M. Health-related quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis:Systematic review and meta-analysis of EuroQoL (EQ-5D) utility scores from Asia. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24:314–326. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.14066. - PubMed
-
- Naqvi AA, Hassali MA, Aftab MT. Epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis, clinical aspects and socioeconomic determinants in Pakistani patients:A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019;69:389–398. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–2038. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous