Mycobacterium manresensis induces trained immunity in vitro
- PMID: 37250788
- PMCID: PMC10182650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106873
Mycobacterium manresensis induces trained immunity in vitro
Abstract
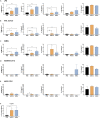
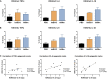
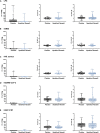
The COVID-19 pandemic posed a global health crisis, with new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants weakening vaccine-driven protection. Trained immunity could help tackle COVID-19 disease. Our objective was to analyze whether heat-killed Mycobacterium manresensis (hkMm), an environmental mycobacterium, induces trained immunity and confers protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection. To this end, THP-1 cells and primary monocytes were trained with hkMm. The increased secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and IL-10, metabolic activity, and changes in epigenetic marks suggested hkMm-induced trained immunity in vitro. Healthcare workers at risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection were enrolled into the MANRECOVID19 clinical trial (NCT04452773) and were administered Nyaditum resae (NR, containing hkMm) or placebo. No significant differences in monocyte inflammatory responses or the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection were found between the groups, although NR modified the profile of circulating immune cell populations. Our results show that M. manresensis induces trained immunity in vitro but not in vivo when orally administered as NR daily for 14 days.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Immunology; Microbiology; Molecular biology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
P-JC and CV are founders of Manremyc, the “Spin-off” of the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP) that is developing the use of Nyaditum resae in collaboration with Reig Jofre SA. P-JC was also the CEO/CSO of Manremyc. P-JC and CV are the inventors of this food supplement. The MANRECOVID19 clinical trial was sponsored by the Reig Jofre Group, which had no role in the study design or data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. All authors had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Figures




References
-
- Gorbalenya A.E., Baker S.C., Baric R.S., de Groot R.J., Drosten C., Gulyaeva A.A., Haagmans B.L., Lauber C., Leontovich A.M., Neuman B.W., et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020;5:536–544. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World health organization weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19. Ed. 102. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...
-
- Asghar N., Mumtaz H., Syed A.A., Eqbal F., Maharjan R., Bamboria A., Shrehta M. Safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines; a systematic review. Immunol. Med. 2022;45:225–237. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

