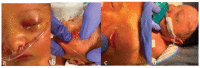
Pseudomembranous conjunctivitis caused by Escherichia coli in a newborn
- PMID: 37250824
- PMCID: PMC10214079
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X231159964
Pseudomembranous conjunctivitis caused by Escherichia coli in a newborn
Abstract
Pseudomembranous conjunctivitis, caused by inflammation of the conjunctiva, is characterized by conjunctival injection, mucopurulent discharge, and formation of a thin membrane overlying the conjunctiva. This is often caused by a viral or bacterial infection. This case report discusses pseudomembranous conjunctivitis from Escherichia coli in a newborn infant which, to our knowledge, has not been reported in relevant literature. This infection was likely transmitted perinatally given that the mother of the infant had blood cultures growing E. coli with the same susceptibilities as the newborn. In addition, we discuss relevant literature on the subject including etiologies, management, and complications of pseudomembranous conjunctivitis.
Keywords: E. coli; Pseudomembranous conjunctivitis; newborn.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Itani MH, Hassoun M, Younis M. Index of suspicion in the nursery. Neoreviews 2008; 9(2): e85–e87.
-
- de-Arriba-Palomero F, Salvá-Palomeque T, de-Arriba-Palomero P, et al.. Epidemiology of pseudomembranous conjunctivitis in a tertiary hospital: a 2-year retrospective study. Eur J Ophthalmol 2021; 31(5): 2275–2279. - PubMed
-
- Palafox SK, Jasper S, Tauber AD, et al.. Ophthalmia neonatorum. J Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2011; 2(1): 24.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources