Advances in All-Inorganic Perovskite Nanocrystal-Based White Light Emitting Devices
- PMID: 37251151
- PMCID: PMC10210016
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00188
Advances in All-Inorganic Perovskite Nanocrystal-Based White Light Emitting Devices
Abstract
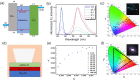
Metal halide perovskites (MHPs) are exceptional semiconductors best known for their intriguing properties, such as high absorption coefficients, tunable bandgaps, excellent charge transport, and high luminescence yields. Among various MHPs, all-inorganic perovskites exhibit benefits over hybrid compositions. Notably, critical properties, including chemical and structural stability, could be improved by employing organic-cation-free MHPs in optoelectronic devices such as solar cells and light-emitting devices (LEDs). Due to their enticing features, including spectral tunability over the entire visible spectrum with high color purity, all-inorganic perovskites have become a focus of intense research for LEDs. This Review explores and discusses the application of all-inorganic CsPbX3 nanocrystals (NCs) in developing blue and white LEDs. We discuss the challenges perovskite-based LEDs (PLEDs) face and the potential strategies adopted to establish state-of-the-art synthetic routes to obtain rational control over dimensions and shape symmetry without compromising the optoelectronic properties. Finally, we emphasize the significance of matching the driving currents of different LED chips and balancing the aging and temperature of individual chips to realize efficient, uniform, and stable white electroluminescence.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Shamsi J.; Urban A. S.; Imran M.; De Trizio L.; Manna L. Metal halide perovskite nanocrystals: synthesis, post-synthesis modifications, and their optical properties. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3296–3348. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00644. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Arora N.; Greco A.; Meloni S.; Hinderhofer A.; Mattoni A.; Rothlisberger U.; Hagenlocher J.; Caddeo C.; Zakeeruddin S. M.; Schreiber F.; et al. Kinetics and energetics of metal halide perovskite conversion reactions at the nanoscale. Commun. Mater. 2022, 3, 22.10.1038/s43246-022-00239-1. - DOI
- Mazumdar S.; Zhao Y.; Zhang X. Stability of perovskite solar cells: degradation mechanisms and remedies. Front. Electron. 2021, 2, 712785.10.3389/felec.2021.712785. - DOI
- Akin S.; Bauer M.; Hertel D.; Meerholz K.; Zakeeruddin S. M.; Graetzel M.; Bäuerle P.; Dar M. I. Robust nonspiro-based hole conductors for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32 (45), 2205729.10.1002/adfm.202205729. - DOI
- Xiang W.; Liu S.; Tress W. A review on the stability of inorganic metal halide perovskites: challenges and opportunities for stable solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2090–2113. 10.1039/D1EE00157D. - DOI
- Boziki A.; Dar M. I.; Jacopin G.; Grätzel M.; Rothlisberger U. Molecular origin of the asymmetric photoluminescence spectra of CsPbBr3 at low temperature. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 2699–2704. 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c00263. - DOI - PubMed
- Uchida R.; Binet S.; Arora N.; Jacopin G.; Alotaibi M. H.; Taubert A.; Zakeeruddin S. M.; Dar M. I.; Graetzel M. Insights about the absence of Rb cation from the 3D perovskite lattice: effect on the structural, morphological, and photophysical properties and photovoltaic performance. Small 2018, 14, 1802033.10.1002/smll.201802033. - DOI - PubMed
- Wang Y.; Dar M. I.; Ono L. K.; Zhang T.; Kan M.; Li Y.; Zhang L.; Wang X.; Yang Y.; Gao X.; et al. Thermodynamically stabilized β-CsPbI3–based perovskite solar cells with efficiencies > 18%. Science 2019, 365 (6453), 591–595. 10.1126/science.aav8680. - DOI - PubMed
- Abdi-Jalebi M.; Ibrahim Dar M.; Senanayak S. P.; Sadhanala A.; Andaji-Garmaroudi Z.; Pazos-Outón L. M.; Richter J. M.; Pearson A. J.; Sirringhaus H.; Grätzel M. Charge extraction via graded doping of hole transport layers gives highly luminescent and stable metal halide perovskite devices. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav201210.1126/sciadv.aav2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Di Girolamo D.; Dar M. I.; Dini D.; Gontrani L.; Caminiti R.; Mattoni A.; Graetzel M.; Meloni S. Dual effect of humidity on cesium lead bromide: enhancement and degradation of perovskite films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12292–12302. 10.1039/C9TA00715F. - DOI
-
- Tan Z.-K.; Moghaddam R. S.; Lai M. L.; Docampo P.; Higler R.; Deschler F.; Price M.; Sadhanala A.; Pazos L. M.; Credgington D.; et al. Bright light-emitting diodes based on organometal halide perovskite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9 (9), 687–692. 10.1038/nnano.2014.149. - DOI - PubMed
- Protesescu L.; Yakunin S.; Bodnarchuk M. I.; Krieg F.; Caputo R.; Hendon C. H.; Yang R. X.; Walsh A.; Kovalenko M. V. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): Novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3692–3696. 10.1021/nl5048779. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Zhang F.; Zhong H.; Chen C.; Wu X.-g.; Hu X.; Huang H.; Han J.; Zou B.; Dong Y. Brightly luminescent and color-tunable colloidal CH3NH3PbX3 (X = Br, I, CL) quantum dots: potential alternatives for display technology. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4533–4542. 10.1021/acsnano.5b01154. - DOI - PubMed
- Bai Z.; Zhong H. Halide perovskite quantum dots: potential candidates for display technology. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1622–1624. 10.1007/s11434-015-0884-y. - DOI
- Gonzalez-Carrero S.; Galian R. E.; Pérez-Prieto J. Maximizing the emissive properties of CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 9187–9193. 10.1039/C4TA05878J. - DOI
- Schmidt L. C.; Pertegás A.; González-Carrero S.; Malinkiewicz O.; Agouram S.; Mínguez Espallargas G.; Bolink H. J.; Galian R. E.; Pérez-Prieto J. Nontemplate Synthesis of CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 850–853. 10.1021/ja4109209. - DOI - PubMed
- Swarnkar A.; Chulliyil R.; Ravi V. K.; Irfanullah M.; Chowdhury A.; Nag A. colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals: luminescence beyond traditional quantum dots. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15424–15428. 10.1002/anie.201508276. - DOI - PubMed
- Song J.; Li J.; Li X.; Xu L.; Dong Y.; Zeng H. Quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on inorganic perovskite cesium lead halides (CsPbX3). Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7162–7167. 10.1002/adma.201502567. - DOI - PubMed
- Li X.; Wu Y.; Zhang S.; Cai B.; Gu Y.; Song J.; Zeng H. CsPbX3 Quantum dots for lighting and displays: room-temperature synthesis, photoluminescence superiorities, underlying origins and white light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2435–2445. 10.1002/adfm.201600109. - DOI
-
- Stranks S. D.; Eperon G. E.; Grancini G.; Menelaou C.; Alcocer M. J. P.; Leijtens T.; Herz L. M.; Petrozza A.; Snaith H. J. Electron-hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 2013, 342, 341–344. 10.1126/science.1243982. - DOI - PubMed
- Xing G.; Mathews N.; Sun S.; Lim S. S.; Lam Y. M.; Grätzel M.; Mhaisalkar S.; Sum T. C. Long-range balanced electron- and hole-transport lengths in organic-inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science 2013, 342, 344–347. 10.1126/science.1243167. - DOI - PubMed
- Yettapu G. R.; Talukdar D.; Sarkar S.; Swarnkar A.; Nag A.; Ghosh P.; Mandal P. Terahertz conductivity within colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals: remarkably high carrier mobilities and large diffusion lengths. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4838–4848. 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xiao Z.; Kerner R. A.; Tran N.; Zhao L.; Scholes G. D.; Rand B. P. Engineering perovskite nanocrystal surface termination for light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 15%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29 (11), 1807284.10.1002/adfm.201807284. - DOI
- Fang Z.; Chen W.; Shi Y.; Zhao J.; Chu S.; Zhang J.; Xiao Z. Dual passivation of perovskite defects for light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 20%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909754.10.1002/adfm.201909754. - DOI
- Chu Z.; Ye Q.; Zhao Y.; Ma F.; Yin Z.; Zhang X.; You J. Perovskite light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 22% via small-molecule passivation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007169.10.1002/adma.202007169. - DOI - PubMed
- Akin S.; Arora N.; Zakeeruddin S. M.; Grätzel M.; Friend R. H.; Dar M. I. New Strategies for Defect Passivation in High-Efficiency Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903090.10.1002/aenm.201903090. - DOI
-
- Wang Y. K.; Yuan F.; Dong Y.; Li J. Y.; Johnston A.; Chen B.; Saidaminov M. I.; Zhou C.; Zheng X.; Hou Y.; Bertens K.; Ebe H.; Ma D. X.; Deng Z.; Yuan S.; Chen R.; Sagar L. K.; Liu J.; Fan J.; Li P.; Li X.; Gao Y.; Fung M.-K.; Lu Z.-H.; Bakr O. M.; Liao L.-S.; Sargent E. H. All-Inorganic quantum-dot LEDs based on a phase stabilized α-CsPbI3 perovskite. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16164–16170. 10.1002/anie.202104812. - DOI - PubMed
- Liu Z.; Qiu W.; Peng X.; Sun G.; Liu X.; Liu D.; Li Z.; He F.; Shen C.; Gu Q.; et al. Perovskite light-emitting diodes with EQE exceeding 28% through a synergetic dual-additive strategy for defect passivation and nanostructure regulation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103268.10.1002/adma.202103268. - DOI - PubMed
- Dey A.; Ye J.; De A.; Debroye E.; Ha S. K.; Bladt E.; Kshirsagar A. S.; Wang Z.; Yin J.; Wang Y.; et al. State of the Art and Prospects for Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2021, 15 (7), 10775–10981. 10.1021/acsnano.0c08903. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Chouhan L.; Ghimire S.; Subrahmanyam C.; Miyasaka T.; Biju V. Synthesis, optoelectronic properties and applications of halide perovskites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2869.10.1039/C9CS00848A. - DOI - PubMed
- Li X.; Wu Y.; Zhang S.; Cai B.; Gu Y.; Song J.; Zeng H. CsPbX3 Quantum Dots for Lighting and Displays: Room-temperature synthesis, photoluminescence superiorities, underlying origins and white light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2435–2445. 10.1002/adfm.201600109. - DOI
- Protesescu L.; Yakunin S.; Bodnarchuk M. I.; Krieg F.; Caputo R.; Hendon C. H.; Yang R. X.; Walsh A.; Kovalenko M. V. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3692–3696. 10.1021/nl5048779. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Pan Q.; Hu H.; Zou Y.; Chen M.; Wu L.; Yang D.; Yuan X.; Fan J.; Sun B.; Zhang Q. Microwave-assisted synthesis of high-quality “all-inorganic” CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) perovskite nanocrystals and their application in light emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 10947–10954. 10.1039/C7TC03774K. - DOI
- Chen M.; Zou Y.; Wu L.; Pan Q.; Yang D.; Hu H.; Tan Y.; Zhong Q.; Xu Y.; Liu H.; et al. Solvothermal synthesis of high-quality all-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals: from nanocube to ultrathin nanowire. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1701121.10.1002/adfm.201701121. - DOI
- Tong Y.; Bladt E.; Aygüler M. F.; Manzi A.; Milowska K. Z.; Hintermayr V. A.; Docampo P.; Bals S.; Urban A. S.; Polavarapu L.; et al. Highly luminescent cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals with tunable composition and thickness by ultrasonication. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13887–13892. 10.1002/anie.201605909. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhu Z.-Y.; Yang Q.-Q.; Gao L.-F.; Zhang L.; Shi A.-Y.; Sun C.-L.; Wang Q.; Zhang H.-L. Solvent-free mechanosynthesis of composition-tunable cesium lead halide perovskite quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1610–1614. 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00431. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

