Synthesis, In Silico Studies, and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Novel Imidazole Derivatives Targeting p38 MAP Kinase
- PMID: 37251188
- PMCID: PMC10210024
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00605
Synthesis, In Silico Studies, and In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Novel Imidazole Derivatives Targeting p38 MAP Kinase
Abstract
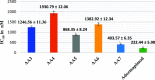
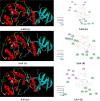
A series of eight novel N-substituted [4-(trifluoro methyl)-1H-imidazole-1-yl] amide derivatives (AA1-AA8) were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated for their in vitro p38 MAP kinase anti-inflammatory inhibitory activity. The synthesized compounds were obtained by coupling [4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazole-1-yl] acetic acid with 2-amino-N-(Substituted)-3-phenylpropanamide derivatives utilizing 1-[bis(dimethylamino)methylene]-1H-1,2,3-triazolo[4,5-b] pyridinium 3-oxide hexafluorophosphate as a coupling agent. Various spectroscopic methods established and confirmed their structures, specifically, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), and mass spectrometry. In order to emphasize the binding site of the p38 MAP kinase protein and newly synthesized compounds, molecular docking studies were carried out. In the series, compound AA6 had the highest docking score of 7.83 kcal/mol. The ADME studies were performed using web software. Studies revealed that all the synthesized compounds were orally active and showed good gastrointestinal absorption within the acceptable range. Lipinski's "rule of five" was used to determine drug-likeness. The synthesized compounds were screened for their anti-inflammatory activity by performing an albumin denaturation assay in which five compounds (AA2, AA3, AA4, AA5, and AA6) were found to exhibit substantial activity. Hence, these were further selected and proceeded for the evaluation of p38 MAP kinase inhibitory activity. The compound AA6 possesses considerable p38 kinase inhibitory anti-inflammatory activity with an IC50 value of 403.57 ± 6.35 nM compared to the prototype drug adezmapimod (SB203580) with an IC50 value of 222.44 ± 5.98 nM. Some further structural modifications in compound AA6 could contribute to the development of new p38 MAP kinase inhibitors with an improved IC50 value.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






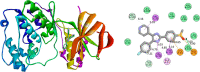
Similar articles
-
Synthesis, evaluation and docking of novel pyrazolo pyrimidines as potent p38α MAP kinase inhibitors with improved anti-inflammatory, ulcerogenic and TNF-α inhibitory properties.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Jun;87:550-559. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.03.037. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30928877
-
Design, synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, single crystal X-ray analysis, in vitro α-amylase inhibition assay, DPPH free radical evaluation and computational studies of naphtho[2,3-d]imidazole-4,9-dione appended 1,2,3-triazoles.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 15;250:115230. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115230. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36863227
-
Probing N-substituted 4-(5-mercapto-4-ethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-N-phenylpiperdine-1-carboxamides as potent 15-LOX inhibitors supported with ADME, DFT calculations and molecular docking studies.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 29;10(17):e35278. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35278. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281606 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Novel Aryl (4-Aryl-1H-Pyrrol-3-yl) (Thiophen-2-yl) Methanone Derivatives: Molecular Modelling, In Silico ADMET, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Ulcer Activities.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2021;20(2):182-195. doi: 10.2174/1871523019999201116191622. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33200699
-
Identification of potential drug candidates to treat gastritis and associated oxidative stress based on some novel 2-aryl-1H-naphtho[2,3-d]imidazole: synthesis, in vitro and in silico analysis.RSC Adv. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):529-537. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07412a. eCollection 2024 Jan 2. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38173575 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, Molecular Simulation, DFT, and Kinetic Study of Imidazotriazole-Based Thiazolidinone as Dual Inhibitor of Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Enzymes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 15;18(3):415. doi: 10.3390/ph18030415. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143192 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Quaternary Ammonium Separation Material based on Coupling Agent Chloromethyl Trimethoxysilane (KH-150) and Its Adsorption and Separation Properties in Studies of Th(IV).Molecules. 2024 Jun 26;29(13):3031. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133031. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38998982 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

