Biomarkers of delirium risk in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37251808
- PMCID: PMC10213257
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1174644
Biomarkers of delirium risk in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
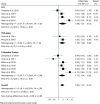
Delirium is a neuropsychiatric syndrome associated with increased morbidity and mortality in older patients. The aim of this study was to review predictive biomarkers of delirium in older patients to gain insights into the pathophysiology of this syndrome and provide guidance for future studies. Two authors independently and systematically searched MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science and Scopus databases up to August 2021. A total of 32 studies were included. Only 6 studies were eligible for the meta-analysis, pooled results showed a significant increase in some serum biomarkers (C-reactive protein [CRP], tumour necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α] and interleukin-6 [IL-6]) among patients with delirium (odds ratio = 1.88, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.637; I2 = 76.75%). Although current evidence does not favour the use of any particular biomarker, serum CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 were the most consistent biomarkers of delirium in older patients.
Keywords: biomarkers; cognitive impairment; delirium; neuroinflammation; older people.
Copyright © 2023 Lozano-Vicario, García-Hermoso, Cedeno-Veloz, Fernández-Irigoyen, Santamaría, Romero-Ortuno, Zambom-Ferraresi, Sáez de Asteasu, Muñoz-Vázquez, Izquierdo and Martínez-Velilla.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of resveratrol supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress among patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Food Funct. 2018 Dec 13;9(12):6116-6128. doi: 10.1039/c8fo01259h. Food Funct. 2018. PMID: 30426122
-
Calorie Restriction With Exercise Intervention Improves Inflammatory Response in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 15;12:754731. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.754731. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34867458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S100β as a potential biomarker of incident delirium: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Minerva Anestesiol. 2020 Aug;86(8):853-860. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.20.14100-2. Epub 2020 May 22. Minerva Anestesiol. 2020. PMID: 32449338
-
Correlation Analysis of Inflammatory Markers CRP and IL-6 and Postoperative Delirium (POD) in Elderly Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies.J Environ Public Health. 2022 Nov 19;2022:1136386. doi: 10.1155/2022/1136386. eCollection 2022. J Environ Public Health. 2022. Retraction in: J Environ Public Health. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9760517. doi: 10.1155/2023/9760517. PMID: 36444287 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Effect of ginger (Zingiber officinale) on inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Cytokine. 2020 Nov;135:155224. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155224. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 32763761
Cited by
-
Management of Coronary Artery Disease in Older Adults: Recent Advances and Gaps in Evidence.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 11;12(16):5233. doi: 10.3390/jcm12165233. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37629275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of melatonin versus placebo for prevention of delirium among medically hospitalised patients: study protocol for a single-centre, double-blinded, randomised controlled trial (project RESTORE).BMJ Open. 2025 Feb 25;15(2):e094195. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094195. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40000080 Free PMC article.
-
Association of peripheral B cells and delirium: combined single-cell sequencing and Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 6;15:1343726. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1343726. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38379709 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines and inflammatory biomarkers and their association with post-operative delirium: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 6;15(1):7830. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82992-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40050293 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with an increase in new diagnoses of schizophrenia spectrum and psychotic disorder: A study using the US national COVID cohort collaborative (N3C).PLoS One. 2024 May 30;19(5):e0295891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295891. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38814888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamis D., van Gool W. A., Eikelenboom P. (2021). Consistent patterns in the inconsistent associations of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), C-reactive protein (C-RP) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels with delirium in surgical populations. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 97:104518. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2021.104518, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altman M. T., Knauert M. P., Murphy T. E., Ahasic A. M., Chauhan Z., Pisani M. A. (2018). Association of intensive care unit delirium with sleep disturbance and functional disability after critical illness: an observational cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 8:63. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0408-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous