Congenital rubella syndrome surveillance in India, 2016-21: Analysis of five years surveillance data
- PMID: 37251844
- PMCID: PMC10209330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15965
Congenital rubella syndrome surveillance in India, 2016-21: Analysis of five years surveillance data
Abstract
Background: In India, facility-based surveillance for congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) was initiated in 2016 to estimate the burden and monitor the progress made in rubella control. We analyzed the surveillance data for 2016-2021 from 14 sentinel sites to describe the epidemiology of CRS.
Method: We analyzed the surveillance data to describe the distribution of suspected and laboratory confirmed CRS patients by time, place and person characteristics. We compared clinical signs of laboratory confirmed CRS and discarded case-patients to find independent predictors of CRS using logistic regression analysis and developed a risk prediction model.
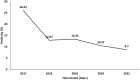
Results: During 2016-21, surveillance sites enrolled 3940 suspected CRS case-patients (Age 3.5 months, SD: 3.5). About one-fifth (n = 813, 20.6%) were enrolled during newborn examination. Of the suspected CRS patients, 493 (12.5%) had laboratory evidence of rubella infection. The proportion of laboratory confirmed CRS cases declined from 26% in 2017 to 8.7% in 2021. Laboratory confirmed patients had higher odds of having hearing impairment (Odds ratio [OR] = 9.5, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.6-16.2), cataract (OR = 7.8, 95% CI: 5.4-11.2), pigmentary retinopathy (OR = 6.7, 95 CI: 3.3-13.6), structural heart defect with hearing impairment (OR = 3.8, 95% CI: 1.2-12.2) and glaucoma (OR = 3.1, 95% CI: 1.2-8.1). Nomogram, along with a web version, was developed.
Conclusions: Rubella continues to be a significant public health issue in India. The declining trend of test positivity among suspected CRS case-patients needs to be monitored through continued surveillance in these sentinel sites.
Keywords: Congenital Rubella Syndrome; India; Surveillance.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Winter A.K., Moss W.J. Rubella. Lancet. 2022;399:1336–1346. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare . 2017. Govt of India. Introduction of Measles Rubella Vaccine (Campaign and Routine Immunization). National Operational Guidelines.https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/195431585071489665073.pdf
-
- World Health Organization . Strategic Plan for Measles Elimination and Rubella and Congenital Rubella Syndrome Control in the South-East Asia Region, 2014-2020. WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia. 2015. Regional office for south-east Asia.https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/205923 accessed.
-
- World Health Organization India . 2017. India Launches One of the World’s Largest Vaccination Campaigns against Measles and Rubella Syndrome with WHO Support. World Health Organization Regional Office for South-East Asia.https://www.who.int/india/news/detail/11-07-2017-india-launches-one-of-t... accessed.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources