The genomic landscape of sensitivity to arsenic trioxide uncovered by genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening
- PMID: 37251921
- PMCID: PMC10214836
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1178686
The genomic landscape of sensitivity to arsenic trioxide uncovered by genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening
Abstract
Introduction: Arsenic trioxide (ATO) is a promising anticancer drug for hematological malignancy. Given the dramatic efficacy of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), ATO has been utilized in other types of cancers, including solid tumors. Unfortunately, the results were not comparable with the effects on APL, and the resistance mechanism has not been clarified yet. This study intends to identify relevant genes and pathways affecting ATO drug sensitivity through genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockdown screening to provide a panoramic view for further study of ATO targets and improved clinical outcomes.
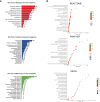
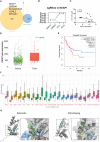
Methods: A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockdown screening system was constructed for ATO screening. The screening results were processed with MAGeCK, and the results were subjected to pathway enrichment analysis using WebGestalt and KOBAS. We also performed protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis using String and Cytoscape, followed by expression profiling and survival curve analysis of critical genes. Virtual screening was used to recognize drugs that may interact with the hub gene.
Results: We applied enrichment analysis and identified vital ATO-related pathways such as metabolism, chemokines and cytokines production and signaling, and immune system responses. In addition, we identified KEAP1 as the top gene relating to ATO resistance. We found that KEAP1 expression was higher in the pan-cancer, including ALL, than in normal tissue. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with higher KEAP1 expression had worse overall survival (OS). A virtual screen showed that etoposide and eltrombopag could bind to KEAP1 and potentially interact with ATO.
Discussion: ATO is a multi-target anticancer drug, and the key pathways regulating its sensitivity include oxidative stress, metabolism, chemokines and cytokines, and the immune system. KEAP1 is the most critical gene regulating ATO drug sensitivity, which is related to AML prognosis and may bind to some clinical drugs leading to an interaction with ATO. These integrated results provided new insights into the pharmacological mechanism of ATO and potentiate for further applications in cancer treatments.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9 screening; KEAP1; arsenic trioxide; leukemia; virtual screening.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Wang, Luo and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NRF2 signaling overcomes acquired resistance to arsenic trioxide in FLT3-mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2024 Jun;103(6):1919-1929. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05742-8. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38630133
-
Arsenic trioxide in hematological malignancies: the new discovery of an ancient drug.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006 Dec;7(6):397-405. doi: 10.2174/138920106779116829. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17168655 Review.
-
G-CSF upregulates the expression of aquaporin-9 through CEBPB to enhance the cytotoxic activity of arsenic trioxide to acute myeloid leukemia cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 May 19;22(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02613-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35590355 Free PMC article.
-
Homoharringtonine potentiates the antileukemic activity of arsenic trioxide against acute myeloid leukemia cells.Exp Cell Res. 2019 Mar 15;376(2):114-123. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Exp Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30763586
-
Balance between the toxicity and anticancer activity of arsenic trioxide in treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 15;409:115299. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115299. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33091440 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics analysis of DNA replication-associated primase polymerase (PRIMPOL) in pan-cancer: a potential target for prognosis and immune response.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Jun 30;28(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01181-9. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37391787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JH, Zhong HJ, Si GY, et al. . In vitro studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4 cell apoptosis with downregulation of bcl-2 expression and modulation of PML-RAR alpha/PML proteins. Blood (1996) 88(3):1052–61. doi: 10.1182/blood.V88.3.1052.1052 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

