Lumbar Facet Syndrome and the Use of Radiofrequency Ablation Technique as an Alternative Therapy: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37252302
- PMCID: PMC10212637
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1768695
Lumbar Facet Syndrome and the Use of Radiofrequency Ablation Technique as an Alternative Therapy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
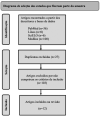
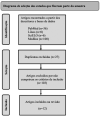
Lumbar facet syndrome stands out as a significant cause for the increasing prevalence of back pain complaints. Alternatives such as radiofrequency (RF) ablation may be a therapeutic option to relieve the chronic pain associated with this condition. It is critical to analyze the effectiveness of lumbar facet syndrome treatment using the traditional RF ablation technique and the relief generated by it in chronic low back pain (CLBP). This study is a systematic review using the following inclusion criteria: title, observational studies, clinical trials, controlled clinical trials, clinical studies, and publications over the last 17 years (from 2005 to 2022). The exclusion criteria included papers addressing other themes and review articles. The databases used for data collection included the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (Medline), PubMed, Scientific Electronic Library Online (SciELO), Lilacs, and Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde (Virtual Health Library in Portuguese). The query used the following terms: facet, pain, lumbar, and radiofrequency. The application of these filters yielded 142 studies, and 12 were included in this review. Most studies indicated that the traditional RF ablation technique was beneficial in relieving CLBP refractory to conservative treatment.
Keywords: low back pain; lumbar vertebrae; radiofrequency therapy; zygapophyseal joint.
Sociedade Brasileira de Ortopedia e Traumatologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de Interesses Os autores não têm conflitos de interesse a declarar.
Figures
References
-
- Breivik H, Collett B, Ventafridda V, Cohen R, Gallacher D. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur J Pain. 2006;10(04):287–333. - PubMed
-
- Beresford Z M, Kendall R W, Willick S E. Síndromes facetárias lombares. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2010;9(01):50–56. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S P, Raja S N. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of lumbar zygapophysial (facet) joint pain. Anesthesiology. 2007;106(03):591–614. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources