Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
- PMID: 37252734
- PMCID: PMC10460682
- DOI: 10.1089/dia.2023.0123
Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
Abstract
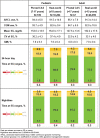
Background: Safety and significant improvement in overall glycated hemoglobin (A1C) and percentage of time spent in (TIR), below (TBR), and above (TAR) glucose range were demonstrated in the pivotal trial of adolescents and adults using the MiniMed™ advanced hybrid closed-loop (AHCL) system with the adjunctive, calibration-required Guardian™ Sensor 3. The present study evaluated early outcomes of continued access study (CAS) participants who transitioned from the pivotal trial investigational system to the approved MiniMed™ 780G system with the non-adjunctive, calibration-free Guardian™ 4 Sensor (MM780G+G4S). Study data were presented alongside those of real-world MM780G+G4S users from Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. Methods: The CAS participants (N = 109, aged 7-17 years and N = 67, aged >17 years) used the MM780G+G4S for 3 months and data of real-world MM780G+G4S system users (N = 10,204 aged ≤15 years and N = 26,099 aged >15 years) were uploaded from September 22, 2021 to December 02, 2022. At least 10 days of real-world continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data were required for analyses. Glycemic metrics, delivered insulin and system use/interactions underwent descriptive analyses. Results: Time in AHCL and CGM use were >90% for all groups. AHCL exits averaged 0.1/day and there were few blood glucose measurements (BGMs) (0.8/day-1.0/day). Adults in both cohorts met most consensus recommendations for glycemic targets. Pediatric groups met recommendations for %TIR and %TBR, although not those for mean glucose variability and %TAR, possibly due to low use of recommended glucose target (100 mg/dL) and active insulin time (2 h) settings (28.4% in the CAS cohort and 9.4% in the real-world cohort). The CAS pediatric and adult A1C were 7.2% ± 0.7% and 6.8% ± 0.7%, respectively, and there were no serious adverse events. Conclusions: Early clinical use of the MM780G+G4S was safe and involved minimal BGMs and AHCL exits. Consistent with real-world pediatric and adult use, outcomes were associated with achievement of recommended glycemic targets. Clinical Trial Registration number: NCT03959423.
Keywords: Advanced hybrid closed-loop; Glucose sensor; Non-adjunctive; Real-world; Time-in-range; Type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The pivotal trial investigators received funding and support from Medtronic (Northridge, CA) to conduct the study at each of their respective centers. G.P.F., conducts research supported by Medtronic, Dexcom, Abbott Diabetes Care, Tandem Diabetes Care, Insulet Corporation, Beta Bionics and Lilly, and has served as a speaker/consultant/advisory board member for Medtronic, Dexcom, Abbott Diabetes Care, Tandem Diabetes Care, Insulet Corporation, Beta Bionics, and Lilly. D.I.S. serves as advisory board member for Medtronic, R.P-B. has received research support from Medtronic and other consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, Bayer, Roche Diabetes Care, Averitas Pharma, Inc., and Nevro. J.R.T has served as advisory board and data safety monitoring board member to Medtronic and provided editorial support to Boehringer Ingelheim.
J.R.T. is President of the Arkansas Diabetes and Endocrinology Center and Medical Investigations, Inc., and has received research support and speaking fees from Medtronic and Lilly, research support from Novo Nordisk and Inversago Pharma, and speaking fees from Bayer. M.S.K. has served as advisory board member to Quest Diagnostics and Corcept Therapeutics and received research support from Abbott Diabetes Care, Aeterna Zentaris, Allergan Sales, LLC., Amgen, Ascendis Pharma, AstraZeneca, 89Bio, Inc., Biolinq, Inc., Corcept Therapeutics, Dexcom, Lily, Giliad Sciences, Inc., Inventiva BioPharma, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Insulet Corporation, Kowa Research Institute, Inc., Lumos Pharma, Mannkind Corporation, Medtronic, Metacrine, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Reata Pharmaceuticals, Regenacy Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sagimet Biosciences, Senseonics, Inc., Tandem Diabetes Care, Tolerion, Inc., Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Zydus Discovery and Zydus Therapeutics Inc., M.P.C. discloses that Diablo Clinical Research has received funding to conduct research from Medtronic, Dexcom, Senseonics, Novo Nordisk, Lilly, Pfizer, Biolinq, Inc., and GraphWear.
B.A.B. has served as advisory board member for Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, and Lilly, and conducted studies sponsored by Medtronic, Tandem Diabetes Care, Insulet Corporation, the JDRF, and National Institutes of Health. C.P. has no competing financial disclosures. J.L.S. serves or has served on advisory panels for Bigfoot Biomedical, Cecelia Health, Insulet Corporation, Medtronic, StartUp Health Diabetes Moonshot, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals; has served as consultant to Abbott Diabetes Care, Bigfoot Biomedical, Insulet Corporation, Medtronic and Zealand Pharma. The Yale School of Medicine has received research support for J.L.S. from Abbott Diabetes Care, JAEB Center for Health Research, the JDRF, Insulet Corporation, Medtronic, the National Institutes of Health and ProventionBio. K.B.K is an employee of MannKind Corporation and has received research support from Medtronic.
The MiniMed™ 780G pump with Guardian™ 4 Sensor is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for individuals ≥7 years of age with T1D. The MiniMed™ 780G system includes technology developed by DreaMed Diabetes (Petah Tikvah, Israel).
Figures
References
-
- Shi L, Fonseca V, Childs B. Economic burden of diabetes-related hypoglycemia on patients, payors, and employers. J Diabetes Complications 2021;35:107916. - PubMed
-
- Sussman M, Sierra JA, Garg S, et al. . Economic impact of hypoglycemia among insulin-treated patients with diabetes. J Med Econ 2016;19:1099–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous