A New Dynamic Slow-Flow Esophageal Balloon Pressure-Volume Curve Calibration Method to Assess Transpulmonary Pressure Monitoring
- PMID: 37253611
- PMCID: PMC10589102
- DOI: 10.4187/respcare.10718
A New Dynamic Slow-Flow Esophageal Balloon Pressure-Volume Curve Calibration Method to Assess Transpulmonary Pressure Monitoring
Keywords: esophageal air-filled catheter calibration; esophageal pressure; transpulmonary pressure monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Figures

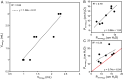
References
-
- Mauri T, Yoshida T, Bellani G, Goligher EC, Carteaux G, Rittayamai R, et al. ; PLeUral pressure working Group (PLUG—Acute Respiratory Failure section of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine). Esophageal and transpulmonary pressure in the clinical setting: meaning, usefulness, and perspectives. Intensive Care Med 2016;42(9):1360–1373. - PubMed
-
- Gattinoni L, Giosa L, Bonifazi M, Pasticci I, Busana M, Macri M, et al. . Targeting transpulmonary pressure to prevent ventilator-induced lung injury. Expert Rev Respir Med 2019;13(8):737–746. - PubMed
-
- Grasso S, Terragni P, Birocco A, Urbino R, Del Sorbo L, Filippini C, et al. . ECMO criteria for influenza A (H1N1)–associated ARDS: role of the transpulmonary pressure. Intensive Care Med 2012;38(3):395–403. - PubMed
-
- Sarge T, Baedorf-Kassis E, Banner-Goodspeed V, Novack V, Loring SH, Gong MN, et al. ; EPVent-2 Study Group. Effect of esophageal pressure–guided positive end-expiratory pressure on survival from acute respiratory distress syndrome: a risk-based and mechanistic re-analysis of the EPVent-2 trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2021;204(10):1153–1163. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

