Cerebral organoids transplantation repairs infarcted cortex and restores impaired function after stroke
- PMID: 37253754
- PMCID: PMC10229586
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-023-00301-7
Cerebral organoids transplantation repairs infarcted cortex and restores impaired function after stroke
Abstract
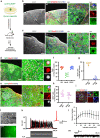
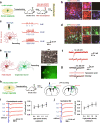
Stroke usually causes prolonged or lifelong disability, owing to the permanent loss of infarcted tissue. Although a variety of stem cell transplantation has been explored to improve neuronal defect behavior by enhancing neuroplasticity, it remains unknown whether the infarcted tissue can be reconstructed. We here cultured human cerebral organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) and transplanted them into the junction of the infarct core and the peri-infarct zone of NOD-SCID mice subjected to stroke. Months later, we found that the grafted organoids survived well in the infarcted core, differentiated into target neurons, repaired infarcted tissue, sent axons to distant brain targets, and integrated into the host neural circuit and thereby eliminated sensorimotor defect behaviors of stroke mice, whereas transplantation of dissociated single cells from organoids failed to repair the infarcted tissue. Our study offers a new strategy for reconstructing infarcted tissue via organoids transplantation thereby reversing stroke-induced disability.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Emberson J, et al. Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;384:1929–1935. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60584-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ni HY, et al. Dissociating nNOS (Neuronal NO Synthase)-CAPON (Carboxy-Terminal Postsynaptic Density-95/Discs Large/Zona Occludens-1 Ligand of nNOS) Interaction Promotes Functional Recovery After Stroke via Enhanced Structural Neuroplasticity. Stroke. 2019;50:728–737. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022647. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

