Analysis of the microglia transcriptome across the human lifespan using single cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 37254100
- PMCID: PMC10230780
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-023-02809-7
Analysis of the microglia transcriptome across the human lifespan using single cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
Background: Microglia are tissue resident macrophages with a wide range of critically important functions in central nervous system development and homeostasis.
Method: In this study, we aimed to characterize the transcriptional landscape of ex vivo human microglia across different developmental ages using cells derived from pre-natal, pediatric, adolescent, and adult brain samples. We further confirmed our transcriptional observations using ELISA and RNAscope.
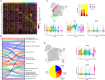
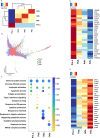
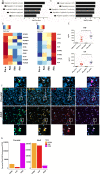
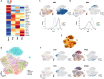
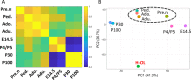
Results: We showed that pre-natal microglia have a distinct transcriptional and regulatory signature relative to their post-natal counterparts that includes an upregulation of phagocytic pathways. We confirmed upregulation of CD36, a positive regulator of phagocytosis, in pre-natal samples compared to adult samples in situ. Moreover, we showed adult microglia have more pro-inflammatory signature compared to microglia from other developmental ages. We indicated that adult microglia are more immune responsive by secreting increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to LPS treatment compared to the pre-natal microglia. We further validated in situ up-regulation of IL18 and CXCR4 in human adult brain section compared to the pre-natal brain section. Finally, trajectory analysis indicated that the transcriptional signatures adopted by microglia throughout development are in response to a changing brain microenvironment and do not reflect predetermined developmental states.
Conclusion: In all, this study provides unique insight into the development of human microglia and a useful reference for understanding microglial contribution to developmental and age-related human disease.
Keywords: Ex vivo human microglia; Gene regulatory network; Transcriptional heterogeneity; scRNA-seq.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare funding.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

