Comprehensive volumetric phenotyping of the neonatal brain in Down syndrome
- PMID: 37254801
- PMCID: PMC10350827
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhad171
Comprehensive volumetric phenotyping of the neonatal brain in Down syndrome
Abstract
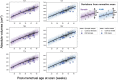
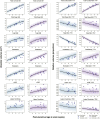
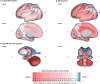
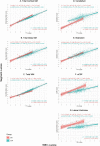
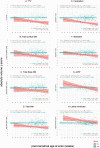
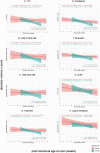
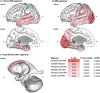
Down syndrome (DS) is the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability with a wide range of neurodevelopmental outcomes. To date, there have been very few in vivo neuroimaging studies of the neonatal brain in DS. In this study we used a cross-sectional sample of 493 preterm- to term-born control neonates from the developing Human Connectome Project to perform normative modeling of regional brain tissue volumes from 32 to 46 weeks postmenstrual age, accounting for sex and age variables. Deviation from the normative mean was quantified in 25 neonates with DS with postnatally confirmed karyotypes from the Early Brain Imaging in DS study. Here, we provide the first comprehensive volumetric phenotyping of the neonatal brain in DS, which is characterized by significantly reduced whole brain, cerebral white matter, and cerebellar volumes; reduced relative frontal and occipital lobar volumes, in contrast with enlarged relative temporal and parietal lobar volumes; enlarged relative deep gray matter volume (particularly the lentiform nuclei); and enlargement of the lateral ventricles, amongst other features. In future, the ability to assess phenotypic severity at the neonatal stage may help guide early interventions and, ultimately, help improve neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with DS.
Keywords: Down syndrome; magnetic resonance imaging; neonate; normative modeling; volumetric.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Accogli A, Addour-Boudrahem N, Srour M. Diagnostic approach to cerebellar hypoplasia. Cerebellum. 2021:20:631–658. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Habbak R, Warren AC, Margaret B, Barta PE, Jerram M, Pearlson GD. Cerebellar volume. Arch Neurol. 1997a:54:209–212. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Li Q, Habbak R, Warren A, Pulsifer MB, Barta PE, Jerram M, Pearlson G. Basal ganglia volume in adults with down syndrome. Psychiatry Res - Neuroimaging. 1997b:74:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Li Q, Honeycutt NA, Warren AC, Pulsifer MB, Barta PE, Chan MD, Smith PD, Jerram M, Pearlson GD. MRI volumes of the hippocampus and amygdala in adults with Down’s syndrome with and without dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 1999:156:564–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

