Association between serum interleukin-6, leptin and insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus - a cross- sectional study
- PMID: 37255771
- PMCID: PMC10225451
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-023-01188-3
Association between serum interleukin-6, leptin and insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus - a cross- sectional study
Abstract
Purpose: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a state of leptin resistance which develops a vicious cycle of hyperinsulinemia and hyperleptinemia leading to aggravation of an inflammatory situation. This study was done to find out the association between IL-6, leptin and insulin in gestational diabetes among North Indian women.
Method: This cross-sectional study included 100 GDM, 100 non-GDM and 50 non-pregnant women. DIPSI (Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group India) criteria was used for screening GDM among pregnant women. GDM and non-GDM pregnant women were further categorized into three groups according to the trimester of pregnancy. Serum IL-6, leptin and insulin were measured in all the enrolled women.
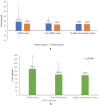
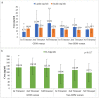
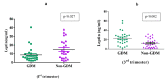
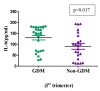
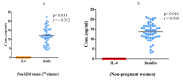
Results: Serum IL-6 levels were significantly higher among GDM women as compared to non-GDM and non-pregnant women. Although the mean serum leptin and insulin levels were higher in GDM, but the difference was not statistically significant. When GDM and non-GDM women were categorized into three trimester, serum leptin levels were found to be significantly higher in 3rd trimester (p < 0.002) and IL-6 in 1st trimester (p < 0.017) among GDM women. No correlation was found between serum IL-6, leptin and insulin in GDM.
Conclusion: Absence of any significant association between leptin and IL-6 signifies that leptin may not be associated with inflammation in gestational diabetes. However, IL-6 may serve as an early marker for screening glucose intolerance during pregnancy.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40200-023-01188-3.
Keywords: DIPSI criteria (Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group India); Gestational diabetes mellitus; Hyperinsulinemia; Hyperleptinemia; Proinflammatory cytokine.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
World Health Organization Versus Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group India Approaches in the Screening of Gestational Diabetes Among Pregnant Women With Risk Factors: A Study Among Rural Population of Telangana, South India.Cureus. 2022 Sep 30;14(9):e29799. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29799. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36340523 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of early (1st trimester) gestational diabetes mellitus in Polish women is accompanied by marked insulin resistance - comparison to PCOS model.Endokrynol Pol. 2022;73(1):1-7. doi: 10.5603/EP.a2021.0095. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Endokrynol Pol. 2022. PMID: 34855192
-
[Maternal plasma leptin levels and their relationship to insulin and glucose in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and gestational impaired glucose tolerance].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2003 May;38(5):261-3. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 12895305 Chinese.
-
Hepatokine levels during the first or early second trimester of pregnancy and the subsequent risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomarkers. 2021 Sep;26(6):517-531. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2021.1928754. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 34082623
-
Meta-analysis comparing diabetes in pregnancy study group India (DIPSI) vs the international association of the diabetes and pregnancy study groups (IADPSG) criteria for diagnosis of gestational diabetes among Indian population.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Jul;62(4):498-505. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2023.03.013. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 37407183 Review.
Cited by
-
Lymphocyte Subsets and Cytokine Changes in Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review.J Diabetes Res. 2025 Mar 4;2025:3494697. doi: 10.1155/jdr/3494697. eCollection 2025. J Diabetes Res. 2025. PMID: 40225013 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

