Investigation renin inhibitor activity from flavonoids derivates by in silico study
- PMID: 37255870
- PMCID: PMC10226698
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.japtr_660_22
Investigation renin inhibitor activity from flavonoids derivates by in silico study
Abstract
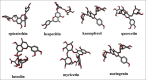
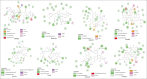
Flavonoids have various pharmacological activities, such as antihypertensive, anticancer, and and antidiabetic effects. Several studies have shown that luteolin, quercetin, kaempferol, myricetin, naringenin, hesperetin, and epicatechin have antihypertensive effects, but the mechanism of action has yet to be discovered with certainty. This study aims to identify flavonoids from luteolin, quercetin, kaempferol, myricetin, naringenin, hesperetin, and epicatechin as renin inhibitors through in silico study; seven flavonoid compounds were docked with 2V0Z with renin inhibitor (Aliskiren) in humans (Homo sapiens 6 LU7) using AutoDock v4.2.6. SwissADME was used to evaluate the pharmacokinetic characteristics of these substances. Results molecular binding of luteolin, quercetin, kaempferol, myricetin, naringenin, hesperetin, and epicatechin, has potential as renin inhibitors with affinity energy values lower than those of aliskiren of -9.3; -9.3; -10.0; -9.2; -9.9; -9.3; and -9.7 kcal/mol. The interactions of these seven compounds have the same catalytic activity as aliskiren on two aspartic acid residues, Asp32 and Asp215. The analysis of pharmacokinetic profiles and the search for physical and chemical properties showed that the seven compounds violated three of the five Lipinski rules, while aliskiren violated one. Hesperitin, kaempferol, and naringenin had similarities with aliskiren on the amino-acid residues in the renin-binding pocket. However, based on pharmacokinetic analysis, the three compounds had an oral pharmacokinetic profile that could have been better than aliskiren.
Keywords: Aliskiren; flavonoid; in silico; renin inhibitor.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Batool A, Sultana M, Gilani P, Javed T. Risk factors, pathophysiology and management of hypertension. Int J Pharm Sci Sci Res. 2018;4:49–61.
-
- Laurent S. Antihypertensive drugs. Pharmacol Res. 2017;124:116–25. - PubMed
-
- Luh Gde SP. Aliskiren Aliskiren (renin inhibitor) as the recent antihypertensive modality. E J Med Udayana. 2013;3:2023–34.
-
- Pich J. The efficacy of renin inhibitors in primary hypertension. Am J Nurs. 2018;118:56. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources