Targeting the p53 signaling pathway in cancers: Molecular mechanisms and clinical studies
- PMID: 37256211
- PMCID: PMC10225743
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.288
Targeting the p53 signaling pathway in cancers: Molecular mechanisms and clinical studies
Abstract
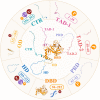
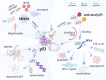
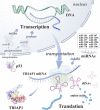
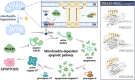
Tumor suppressor p53 can transcriptionally activate downstream genes in response to stress, and then regulate the cell cycle, DNA repair, metabolism, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and other biological responses. p53 has seven functional domains and 12 splice isoforms, and different domains and subtypes play different roles. The activation and inactivation of p53 are finely regulated and are associated with phosphorylation/acetylation modification and ubiquitination modification, respectively. Abnormal activation of p53 is closely related to the occurrence and development of cancer. While targeted therapy of the p53 signaling pathway is still in its early stages and only a few drugs or treatments have entered clinical trials, the development of new drugs and ongoing clinical trials are expected to lead to the widespread use of p53 signaling-targeted therapy in cancer treatment in the future. TRIAP1 is a novel p53 downstream inhibitor of apoptosis. TRIAP1 is the homolog of yeast mitochondrial intermembrane protein MDM35, which can play a tumor-promoting role by blocking the mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway. This work provides a systematic overview of recent basic research and clinical progress in the p53 signaling pathway and proposes that TRIAP1 is an important therapeutic target downstream of p53 signaling.
Keywords: TRIAP1; apoptosis; cancer biomarker; molecular mechanism; p53; targeted therapy.
© 2023 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kern SE. p53: tumor suppression through control of the cell cycle. Gastroenterology. 1994;106(6):1708‐11. - PubMed
-
- Sengupta S, Harris CC. p53: traffic cop at the crossroads of DNA repair and recombination. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(1):44‐55. - PubMed
-
- Speidel D. Transcription‐independent p53 apoptosis: an alternative route to death. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20(1):14‐24. - PubMed
-
- Hafner A, Bulyk ML, Jambhekar A, Lahav G. The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(4):199‐210. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
