Indian Hedgehog release from TNF-activated renal epithelia drives local and remote organ fibrosis
- PMID: 37256934
- PMCID: PMC11977576
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn0736
Indian Hedgehog release from TNF-activated renal epithelia drives local and remote organ fibrosis
Abstract
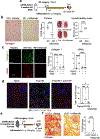
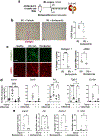
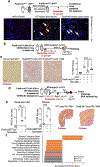
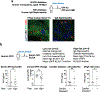
Progressive fibrosis is a feature of aging and chronic tissue injury in multiple organs, including the kidney and heart. Glioma-associated oncogene 1 expressing (Gli1+) cells are a major source of activated fibroblasts in multiple organs, but the links between injury, inflammation, and Gli1+ cell expansion and tissue fibrosis remain incompletely understood. We demonstrated that leukocyte-derived tumor necrosis factor (TNF) promoted Gli1+ cell proliferation and cardiorenal fibrosis through induction and release of Indian Hedgehog (IHH) from renal epithelial cells. Using single-cell-resolution transcriptomic analysis, we identified an "inflammatory" proximal tubular epithelial (iPT) population contributing to TNF- and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-induced IHH production in vivo. TNF-induced Ubiquitin D (Ubd) expression was observed in human proximal tubular cells in vitro and during murine and human renal disease and aging. Studies using pharmacological and conditional genetic ablation of TNF-induced IHH signaling revealed that IHH activated canonical Hedgehog signaling in Gli1+ cells, which led to their activation, proliferation, and fibrosis within the injured and aging kidney and heart. These changes were inhibited in mice by Ihh deletion in Pax8-expressing cells or by pharmacological blockade of TNF, NF-κB, or Gli1 signaling. Increased amounts of circulating IHH were associated with loss of renal function and higher rates of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Thus, IHH connects leukocyte activation to Gli1+ cell expansion and represents a potential target for therapies to inhibit inflammation-induced fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
JVB is an advisor with equity in Oisin Biotherapeutics, an advisor to Serepta, Stugen and Sareptou, and has been a consultant to Janssen and AstraZeneca. JVB is an inventor on KIM-1 patents that are assigned to MassGeneralBrigham. DAF has received research funding from Argenx, undertaken consultancy work for Rejuvenon Life Sciences and is on the scientific advisory board of Dorian Therapeutics. All other authors have no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Indian Hedgehog links kidney injury to fibrosis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Aug;19(8):478. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00735-8. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37386290 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hearps AC, Martin GE, Angelovich TA, Cheng WJ, Maisa A, Landay AL, Jaworowski A, Crowe SM, Aging is associated with chronic innate immune activation and dysregulation of monocyte phenotype and function. Aging cell 11, 867–875 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Santos Morais G Junior, Ignacio Valenzuela Perez D, Cecilia Tonet-Furioso A, Gomes L, Coelho Vilaca KH, Paulo Alves V, Franco Moraes C, Toledo Nobrega O, Circulating Interleukin-6 (but Not Other Immune Mediators) Associates with Criteria for Fried’s Frailty among Very Old Adults. J Aging Res 2020, 6831791 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kurts C, Panzer U, Anders HJ, Rees AJ, The immune system and kidney disease: basic concepts and clinical implications. Nat Rev Immunol 13, 738–753 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Sato Y, Yanagita M, Immunology of the ageing kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol 15, 625–640 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

