Can Takayasu Arteritis Cause Hydronephrosis?
- PMID: 37258208
- PMCID: PMC10293010
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0305-22
Can Takayasu Arteritis Cause Hydronephrosis?
Abstract
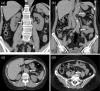
A 74-year-old woman was admitted because of malaise and a low-grade fever. Her C-reactive protein level was 0.96 mg/dL. Computed tomography (CT) revealed diffuse uniform thickening of the arterial wall from the abdominal aorta to the common iliac artery and right hydronephrosis. 18F-fluordesoxyglucose positron emission tomography-CT showed an accumulation in the same area. These findings suggested Takayasu arteritis and retroperitoneal fibrosis as differential diagnoses. Takayasu arteritis is characterized by thickening of the arterial walls, and retroperitoneal fibrosis is characterized by membranous lesions covering the outer surface of the arterial walls. Thus, Takayasu arteritis was deemed the most likely diagnosis. Steroid treatment was effective.
Keywords: 18F-fluordesoxyglucose positron emission tomography; Takayasu arteritis; hydronephrosis; retroperitoneal fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Isobe M, Amano K, Arimura Y, et al.; JCS Joint Working Group. JCS 2017 guideline on management of vasculitis syndrome - digest version. Circ J 84: 299-359, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe Y, Miyata T, Tanemoto K. Current clinical features of new patients with Takayasu arteritis observed from cross-country research in Japan: age and sex specificity. Circulation 132: 1701-1709, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Mason JC. Takayasu arteritis--advances in diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6: 406-415, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Maksimowicz-McKinnon K, Clark TM, Hoffman GS. Limitations of therapy and a guarded prognosis in an American cohort of Takayasu arteritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 56: 1000-1009, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

