Disulfidptosis: a new form of programmed cell death
- PMID: 37259067
- PMCID: PMC10230712
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02712-2
Disulfidptosis: a new form of programmed cell death
Abstract
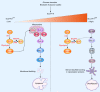
Disulfidptosis, a new form of cell death triggered by disulfide stress, is characterized by the collapse of cytoskeleton proteins and F-actin due to the intracellular accumulation of disulfides. This discovery will eventually aid in the development of therapeutic strategies against cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

