Current Progress and Outlook for Agrimonolide: A Promising Bioactive Compound from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb
- PMID: 37259301
- PMCID: PMC9960068
- DOI: 10.3390/ph16020150
Current Progress and Outlook for Agrimonolide: A Promising Bioactive Compound from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb
Abstract
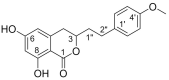
Agrimonolide (AM), which is a derivative of isocoumarins, is found mainly in the herb Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. This compound is highly lipophilic and readily crosses the blood-brain barrier. In recent years, interest has grown in the use of AM as a multitarget natural treatment for various diseases, such as cancer, inflammation, hepatic injury, myocardial damage, and diabetes mellitus. The potential mechanisms of these pharmacological effects have been clarified at cellular and molecular levels. AM shows no cytotoxicity over a range of concentrations in different types of cells, providing evidence for its good safety profile in vitro. These findings indicate that AM is a promising medicinal agent. However, most studies on AM's pharmacological activities, mechanisms of action, and safety lack substantial animal or human data. Additionally, the pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and disposition of this compound have received little attention. This review highlights the status of current information regarding the sources, properties, pharmacological effects, and safety of AM. Furthermore, potential strategies to resolve problematic issues identified in previous studies are fully discussed. This summary and analysis of the research progress of AM may inspire deeper investigations and more extensive applications of AM in the future.
Keywords: Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.; agrimonolide; pharmacological effect; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.: A review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology.Heliyon. 2022 Jul 21;8(8):e09972. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09972. eCollection 2022 Aug. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36046524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-colorectal cancer effect and metabolites of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jul 15;329:118146. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118146. Epub 2024 Apr 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38604512
-
Agrimonolide from Agrimonia pilosa suppresses inflammatory responses through down-regulation of COX-2/iNOS and inactivation of NF-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages.Phytomedicine. 2016 Jul 15;23(8):846-55. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.03.016. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27288920
-
[Studies on the structure of a new ellagic acid glycoside from the root-sprouts of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1990;25(10):798-800. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1990. PMID: 2099598 Chinese.
-
The Medicinal Plant Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb.: Botanical Description, Traditional use, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(9):1660-1688. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220928163930. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 36177633 Review.
Cited by
-
Exserolide J ameliorates lipid accumulation in vitro by regulating liver X receptor alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha proteins.Heliyon. 2024 May 23;10(11):e31861. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31861. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38947487 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ferroptosis: a promising avenue for ovarian cancer treatment.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1578723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1578723. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects and Mechanisms of the Xianhecao-Huanglian Drug Pair on Autophagy-Mediated Intervention in Acute Inflammatory Bowel Disease via the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway.Biol Proced Online. 2024 Aug 26;26(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12575-024-00242-5. Biol Proced Online. 2024. PMID: 39187810 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Macroporous Resin Combined Extraction and Purification of Polyphenols from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb. and Anti-Tumor Effect In Vitro.Molecules. 2025 Mar 26;30(7):1478. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071478. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han S., Zhang P., Wei F., Wang S. Screening active components acting on α1A adrenergic receptors from agrimony using a Sprague-Dawley rat prostate cell membrane chromatography online coupled HPLC/MS method. Anal. Methods. 2012;4:3351–3357. doi: 10.1039/c2ay25703c. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

