Prolonging genetic circuit stability through adaptive evolution of overlapping genes
- PMID: 37260076
- PMCID: PMC10359631
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad484
Prolonging genetic circuit stability through adaptive evolution of overlapping genes
Abstract
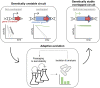
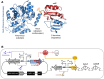
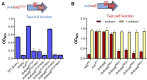
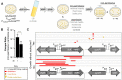
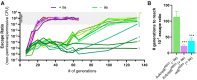
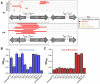
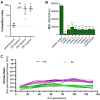
The development of synthetic biological circuits that maintain functionality over application-relevant time scales remains a significant challenge. Here, we employed synthetic overlapping sequences in which one gene is encoded or 'entangled' entirely within an alternative reading frame of another gene. In this design, the toxin-encoding relE was entangled within ilvA, which encodes threonine deaminase, an enzyme essential for isoleucine biosynthesis. A functional entanglement construct was obtained upon modification of the ribosome-binding site of the internal relE gene. Using this optimized design, we found that the selection pressure to maintain functional IlvA stabilized the production of burdensome RelE for >130 generations, which compares favorably with the most stable kill-switch circuits developed to date. This stabilizing effect was achieved through a complete alteration of the allowable landscape of mutations such that mutations inactivating the entangled genes were disfavored. Instead, the majority of lineages accumulated mutations within the regulatory region of ilvA. By reducing baseline relE expression, these more 'benign' mutations lowered circuit burden, which suppressed the accumulation of relE-inactivating mutations, thereby prolonging kill-switch function. Overall, this work demonstrates the utility of sequence entanglement paired with an adaptive laboratory evolution campaign to increase the evolutionary stability of burdensome synthetic circuits.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Puurunen M.K., Vockley J., Searle S.L., Sacharow S.J., Phillips J.A., Denney W.S., Goodlett B.D., Wagner D.A., Blankstein L., Castillo M.J.et al.. Safety and pharmacodynamics of an engineered E. coli Nissle for the treatment of phenylketonuria: a first-in-human phase 1/2a study. Nat. Metab. 2021; 3:1125–1132. - PubMed
-
- Steidler L., Hans W., Schotte L., Neirynck S., Obermeier F., Falk W., Fiers W., Remaut E.. Treatment of murine colitis by Lactococcus lactis secreting interleukin-10. Science. 2000; 289:1352–1355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

