Combination of Rituximab and Low-dose Tacrolimus in the Treatment of Refractory Membranous Nephropathy: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 37260416
- PMCID: PMC10339845
- DOI: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2023.2022-9-7
Combination of Rituximab and Low-dose Tacrolimus in the Treatment of Refractory Membranous Nephropathy: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Conventional regimens for refractory idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN) still have limitations. Rituximab (RTX) has a good effect in the treatment of refractory IMN. However, whether RTX single or combined with immunosuppressive therapy is more effective and whether adverse events will increase are still inconclusive.
Aims: To investigate the efficacy and safety of RTX combined with low-dose tacrolimus (TAC) versus RTX alone in the treatment of refractory IMN.
Study design: A retrospective cohort study.
Methods: We retrospectively studied 91 cases of refractory IMN diagnosed between January 2018 and June 2021, all of which immunosuppressive regimens had failed. Thirty-four patients received RTX combined with TAC (RTX + TAC group), and 57 patients were treated with RTX alone (RTX group). The RTX + TAC group was given RTX 1 g once every 2 weeks, two times, and TAC 0.03 mg/kg/day orally. In the RTX group, RTX was given at the same dosage as the RTX + TAC group. Clinical data were collected at 12 months of follow-up to compare the complete and partial remission rates and the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups.
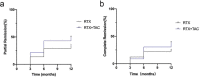
Results: The overall effectiveness rate of RTX + TAC in the treatment of refractory IMN was 87.14%, of which the partial and complete remission rates were 50.01% and 37.13%, respectively, and the median time to complete remission was 9 (interquartile range [IQR] 6.0, 12.0) months. The overall effectiveness rate of RTX was 65.87%, of which the partial and complete remission rates were 39.48% and 26.39%, respectively, and the median time to complete remission was 10.5 (IQR 6.0, 12.0) months. Adverse events occurred in 6 (17.65%) patients in the RTX + TAC group and in 11 (19.30%) in the RTX group (P = 0.473). Proteinuria and high titer of PLA2R are risk factors for non-remission.
Conclusion: The complete and partial remission rates of RTX combined with low-dose TAC in the treatment of refractory IMN are higher than those of RTX alone, and no significant increase in adverse events was noted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combination of ultra-low dose rituximab and low dose tacrolimus versus tacrolimus alone in the treatment of non-responsive idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a Chinese retrospective cohort study.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jul 15;13(7):7622-7631. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34377239 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of efficacy and safety of immunosuppressive therapy and rituximab targeting therapy in idiopathic membranous nephropathy].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;40(7):636-641. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39179407 Chinese.
-
Optimized rituximab regimen versus recommended regimen for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A single-center retrospective cohort study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 30;130:111718. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111718. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38377859
-
Treatment of rituximab in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a case series and literature review.Korean J Intern Med. 2022 Jul;37(4):830-840. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2021.155. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Korean J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35421909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus monotherapy versus cyclophosphamide-corticosteroid combination therapy for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jul 16;100(28):e26628. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026628. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34260552 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Obinutuzumab: a new frontier in the treatment of refractory idiopathic membranous nephropathy.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Sep;57(9):3075-3076. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04500-7. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40205126 No abstract available.
-
Exploration of rituximab treatment strategies for membranous nephropathy adapted to the Chinese healthcare environment.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jan 31;26(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-03980-0. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39891089 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of rituximab for membranous nephropathy in adults: a meta-analysis of RCT.Front Nephrol. 2025 Apr 29;5:1548679. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2025.1548679. eCollection 2025. Front Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40365242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keri KC, Blumenthal S, Kulkarni V, Beck L, Chongkrairatanakul T. Primary membranous nephropathy: comprehensive review and historical perspective. Postgrad Med J. 2019;95:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Cattran D, Brenchley P. Membranous nephropathy: thinking through the therapeutic options. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32(Suppl 1):22–29. - PubMed
-
- Caravaca-Fontán F, Fernández-Juárez GM, Floege J, et al. The management of membranous nephropathy-an update. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022;37:1033–1042. - PubMed
-
- Roccatello D, Sciascia S, Di Simone D, et al. New insights into immune mechanisms underlying response to Rituximab in patients with membranous nephropathy: A prospective study and a review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15:529–538. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
