Bacterial Wars-a tool for the prediction of bacterial predominance based on network analysis measures
- PMID: 37260512
- PMCID: PMC10227370
- DOI: 10.1093/nargab/lqad049
Bacterial Wars-a tool for the prediction of bacterial predominance based on network analysis measures
Abstract
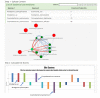
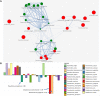
Bacterial Wars (BW) is a network-based tool that applies a two-step pipeline to display information on the competition of bacterial species found in the same microbiome. It utilizes antimicrobial peptide (AMP) sequence similarities to obtain a relationship between species. The working hypothesis (putative AMP defense) is that friendly species share sequence similarity among the putative AMPs of their proteomes and are therefore immune to their AMPs. This may not happen in competing bacterial species with dissimilar putative AMPs. Similarities in the putative AMPs of bacterial proteomes may be thus used to predict predominance. The tool provides insights as to which bacterial species are more likely to 'die' in a competing environmental niche.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Putative Antimicrobial Peptides Within Bacterial Proteomes Affect Bacterial Predominance: A Network Analysis Perspective.Front Microbiol. 2021 Nov 12;12:752674. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.752674. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34867874 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Psacothea hilaris: De Novo Assembly and Antimicrobial Peptide Prediction.Insects. 2020 Oct 5;11(10):676. doi: 10.3390/insects11100676. Insects. 2020. PMID: 33027983 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Screening for Prediction and Design of Antimicrobial Peptides with AmpGram.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 17;21(12):4310. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124310. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32560350 Free PMC article.
-
Insect Antimicrobial Peptides, a Mini Review.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Nov 8;10(11):461. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110461. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30413046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and consequences of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides.Drug Resist Updat. 2016 May;26:43-57. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Drug Resist Updat. 2016. PMID: 27180309 Review.
References
-
- Kerr B., Riley M.A., Feldman M.W., Bohannan B.J.. Local dispersal promotes biodiversity in a real-life game of rock-paper-scissors. Nature. 2002; 418:171–174. - PubMed
-
- Kirkup B.C., Riley M.A.. Antibiotic-mediated antagonism leads to a bacterial game of rock-paper-scissors in vivo. Nature. 2004; 428:412–414. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

