Outcome of Rodenticide Poisoning and Its Associated Factors Among Adult Patients Admitted with Rodenticide Poisoning at the Emergency Unit of Debre Tabor Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Debre Tabor, North Central Ethiopia
- PMID: 37260736
- PMCID: PMC10228517
- DOI: 10.2147/OAEM.S405970
Outcome of Rodenticide Poisoning and Its Associated Factors Among Adult Patients Admitted with Rodenticide Poisoning at the Emergency Unit of Debre Tabor Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Debre Tabor, North Central Ethiopia
Abstract
Introduction: Rodenticides are pesticides used to eradicate rodents. It is a common reason for visits to the emergency department and hospitalization, and it is a major public health concern. Intentional or unintentional intoxication can result in severe consequences with a high fatality rate. In Ethiopia, studies on the outcome of rodenticide poisoning are scarce. The goal of this study was to assess the outcomes of rodenticide poisoning and its associated factors in adult patients admitted to the emergency unit of Debre Tabor Comprehensive Specialized Hospital in North Central Ethiopia.
Methods: A retrospective record review institutional-based cross-sectional study design was used on 156 adult patients treated with rodenticide poisoning at Debre Tabor Comprehensive Specialized Hospital's emergency unit between May 1, 2017 and April 30, 2022. To collect data from patient medical documents and the Health Management Information System, an abstraction sheet was employed. The information was entered into EPI data version 4.6, then exported and analyzed using STATA version 14 software. To analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables, bivariable and multivariable regression were used.
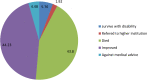
Results: A total of 156 participants were involved in the study. The majority of them 55.13% were in the age group of 19-37 years with the median age of 23 years. Three-fourth of the cases were suicidal poisoning. Overall, 49.35% patients presented to Debre Tabor Specialized Hospital had poor outcome. Having suicidal poisoning (AOR = 10.64; 95% CI: 2.43, 46.53), having tachycardia (AOR = 5.41; 95% CI: 1.54, 18.98), being referred from other health center (AOR = 5.78; 95% CI: 1.97, 16.95) were factors associated with poor outcome.
Conclusion: Rodenticide poisoning had a poor overall outcome. Suicidal poisoning, tachycardia, and referral from other health facilities were all important predictors in poor rodenticide poisoning outcomes.
Keywords: emergency; poisoning; rodenticide.
© 2023 Tassew et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patterns, Potential Teratogenicity, and Associated Factors of Drugs Prescribed to Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Care Units in Debre Tabor Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Debre Tabor, Northwest Ethiopia.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Nov 11;2024:5577862. doi: 10.1155/2024/5577862. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39559257 Free PMC article.
-
Self-referral and associated factors among patients attending adult outpatient departments in Debre tabor general hospital, North West Ethiopia.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Jun 28;21(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06642-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34183005 Free PMC article.
-
Maximizing the detection rate of hypoglycemia among preterm neonates admitted in Neonatal intensive care unit in Ethiopia, 2021.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 9;13(1):2283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29112-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36759521 Free PMC article.
-
Triage implementation audit at the adult emergency department of Debre Tabor Comprehensive Specialized Hospital in Ethiopia.Afr J Emerg Med. 2024 Dec;14(4):506-511. doi: 10.1016/j.afjem.2024.10.001. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Afr J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39720011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterns and epidemiology of acute poisoning in Ethiopia: systematic review of observational studies.Arch Public Health. 2018 Jul 2;76:34. doi: 10.1186/s13690-018-0275-3. eCollection 2018. Arch Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29988616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Global health estimates: leading causes of death; 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-est.... Accessed May 22, 2023.
-
- Suicide worldwide in 2019; 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240026643. Accessed May 22, 2023.
-
- Paul Prabhakar Abhilash K, Jayakaran J. Rodenticide poisoning literature review and management. Curr Med Issues. 2020;17:129–133.
-
- 2020 annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th annual report – PubMed; 2022. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34890263/. Accessed May 22, 2023. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous