The Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Moxibustion for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Related Pain: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37261035
- PMCID: PMC10228586
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S408814
The Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Moxibustion for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Related Pain: A Randomized, Controlled Trial
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effects of moxibustion in relieving pain, and other clinical symptoms for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and explore the potential mechanism of moxibustion treatment for RA.
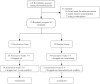
Patients and methods: Seventy qualified RA patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to the moxibustion group or the routine group. The routine group only took oral methotrexate tablets and folic acid tablets. The moxibustion group was treated with moxibustion based on oral pharmaceutical. Moxibustion was performed two times weekly for 8 weeks, a total of 16 sessions. Patients scored their pain on a visual analog scale (VAS). The American College of Rheumatology improvement criteria of 20%, 50% and 70% (ACR20, ACR50 and ACR70) after treatment were investigated. Clinical symptoms, a disease activity score using 28 joint counts (DAS28), simplified disease activity index (SDAI), clinical disease activity index (CDAI), health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) of RA patients were analyzed before and after treatment.
Results: After treatment, the VAS scores, tender and swollen joint counts, morning stiffness scores, disease activity scores (DAS28, SDAI, CDAI), HAQ scores in the two groups were both improved, and the effects of moxibustion group were more obvious (P < 0.05). The ACR20 and ACR50 of the moxibustion group were greater than that of the routine group (P < 0.05), no significant difference of the ACR70 existed between the two groups (P > 0.05). In addition, the decreases of IL-1β, TNF-α, VEGF of the moxibustion group were better than that of the routine group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Moxibustion could effectively relieve pain, ameliorate the clinical symptoms, and decrease the disease activity of RA. The potential mechanism may be the decrease in the level of serum inflammatory factors.
Keywords: inflammatory factor; moxibustion; pain; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2023 Liao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources