Airway stenting for central airway obstruction: a review
- PMID: 37261090
- PMCID: PMC10226894
- DOI: 10.21037/med-22-65
Airway stenting for central airway obstruction: a review
Abstract
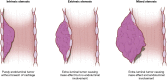
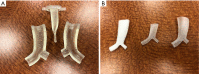
Central airway obstruction is a serious complication of various diseases, most often malignancy. Malignant etiologies include primary lung cancer as most common though metastases from various other cancers can obstruct the airways as well. Benign etiologies include inflammatory or fibrotic changes due to prior airway interventions (e.g., endotracheal intubation or tracheostomy) or specific autoimmune conditions. Different interventional modalities exist including various electrosurgical or mechanical debulking tools, though these are sometimes insufficient or contraindicated for the purpose of restoration of airway patency. The placement of stents is thus needed in certain particularly complex or refractory cases. Airway stenting requires careful patient selection and stent selection along with a thorough knowledge of relevant anatomy and procedural technique. Indeed, certain clinical presentations are better suited for stent placement and more likely to achieve a symptomatic benefit. Moreover, a variety of stents exist with each having different attributes that may better fit specific conditions. Complications must be managed properly as well. These include stent migration, granulation tissue formation, and stent-related infection which can have clinically significant consequences. In this review, we will discuss airway stenting for central airway obstruction with regard to these various subject areas as well as conclude with discussion of future research directions.
Keywords: Airway obstruction; bronchoscopy; interventional pulmonology; stenosis; stent.
2023 Mediastinum. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://med.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/med-22-65/coif). The series “Management of Airway and Vascular Invasion in the Mediastinum” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. BFS served as the unpaid Guest Editor of the series. RFC served as the unpaid Guest Editor of the series and serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Mediastinum from April 2022 to March 2024. RFC reports research grants from Siemens and Intuitive and he is a paid consultant for Siemens, Intuitive and Johnson and Johnson. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Michaud G. Malignant central airway obstruction. In: Ernst A, Herth F. editors. Principles and Practice of Interventional Pulmonology. New York, NY, USA: Springer, 2013.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
