Managing Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome: The Potential Impact of the Food and Drug Omnibus Reform Act
- PMID: 37261183
- PMCID: PMC10228706
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.38336
Managing Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome: The Potential Impact of the Food and Drug Omnibus Reform Act
Abstract
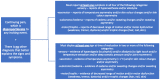
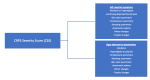
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a neurological disorder characterized by persistent limb symptoms. With there being no definitive tests, diagnosis can be challenging. The Budapest criteria are the standard for diagnosis. The underlying mechanisms of CRPS involve changes in skin innervation, sensitization of the nervous system, inflammatory cytokines, and genetic and psychological factors. Treatment typically involves a multidisciplinary approach. We present a case of a 71-year-old male with CRPS involving the right upper extremity and a complex history of management including physical therapy, oxycodone, muscle relaxers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and multiple stellate ganglion blocks. The patient manages his pain with off-label medications, including methadone, duloxetine, and pregabalin. In the United States, the management of chronic pain may be affected by potential usage restrictions imposed by the Food and Drug Omnibus Reform Act (FDORA). Under this new act, physicians may face limitations in prescribing off-label medications for specific diagnoses. We aim to highlight the need for prioritizing patient care and individualized treatment in healthcare policy decision-making.
Keywords: budapest criteria; chronic pain; chronic regional pain syndrome; food and drug omnibus reform act; off-label treatments; type 1 crps; upper extremity injury.
Copyright © 2023, Herson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome. Schwartzman RJ, Alexander GM, Grothusen J. Expert Rev Neurother. 2006;6:669–681. - PubMed
-
- Pain and quality of life in patients with critical limb ischaemia: results of a randomized controlled multicentre study on the effect of spinal cord stimulation. ESES study group. Spincemaille GH, Klomp HM, Steyerberg EW, Habbema JD. Eur J Pain. 2000;4:173–184. - PubMed
-
- Complex regional pain syndrome: practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines, 4th edition. Harden RN, Oaklander AL, Burton AW, et al. Pain Med. 2013;14:180–229. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
