Artificial intelligence in mobile health for skin cancer diagnostics at home (AIM HIGH): a pilot feasibility study
- PMID: 37261324
- PMCID: PMC10227364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102019
Artificial intelligence in mobile health for skin cancer diagnostics at home (AIM HIGH): a pilot feasibility study
Abstract
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI)-based mobile phone apps (mHealth) have the potential to streamline care for suspicious skin lesions in primary care. This study aims to investigate the conditions and feasibility of a study that incorporates an AI-based app in primary care and evaluates its potential impact.
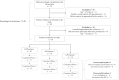
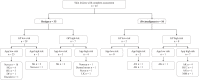
Methods: We conducted a pilot feasibility study from November 22nd, 2021 to June 9th, 2022 with a mixed-methods design on implementation of an AI-based mHealth app for skin cancer detection in three primary care practices in the Netherlands (Rotterdam, Leiden and Katwijk). The primary outcome was the inclusion and successful participation rate of patients and general practitioners (GPs). Secondary outcomes were the reasons, facilitators and barriers for successful participation and the potential impact in both pathways for future sample size calculations. Patients were offered use of an AI-based mHealth app before consulting their GP. GPs assessed the patients blinded and then unblinded to the app. Qualitative data included observations and audio-diaries from patients and GPs and focus-groups and interviews with GPs and GP assistants.
Findings: Fifty patients were included with a median age of 52 years (IQR 33.5-60.3), 64% were female, and 90% had a light skin type. The average patient inclusion rate was 4-6 per GP practice per month and 84% (n = 42) successfully participated. Similarly, in 90% (n = 45 patients) the GPs also successfully completed the study. GPs never changed their working diagnosis, but did change their treatment plan (n = 5) based on the app's assessments. Notably, 54% of patients with a benign skin lesion and low risk rating, indicated that they would be reassured and cancel their GP visit with these results (p < 0.001).
Interpretation: Our findings suggest that studying implementation of an AI-based mHealth app for detection of skin cancer in the hands of patients or as a diagnostic tool used by GPs in primary care appears feasible. Preliminary results indicate potential to further investigate both intended use settings.
Funding: SkinVision B.V.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Convolutional neural network; General practitioners; Mobile health; Primary care; Skin cancer.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Erasmus MC Department of Dermatology has received an unrestricted research grant from SkinVision B.V. None of the authors received any direct fees for consulting or salary from the company. Tobias E Sangers declares speaker honoraria from Pfizer, Janssen-Cilag, and UCB. There are no other declarations of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmadi K., Prickaerts E., Smeets J.G.E., Joosten V., Kelleners-Smeets N.W.J., Dinant G.J. Current approach of skin lesions suspected of malignancy in general practice in the Netherlands: a quantitative overview. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(2):236–241. - PubMed
-
- Meijer W., Verberne L., Weesie Y., et al. NIVEL; 2019. Zorg door de huisarts. Nivel Zorgregistraties Eerste Lijn: jaarcijfers 2018 en trendcijfers 2014-2018.https://www.nivel.nl/nl/publicatie/zorg-door-de-huisarts-nivel-zorgregis... [Available from:
-
- Wakkee M., van Egmond S., Louwman M., et al. Opportunities for improving the efficiency of keratinocyte carcinoma care in primary and specialist care: results from population-based Dutch cohort studies. Eur J Cancer. 2019;117:32–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

