The role of PD-1 signaling in health and immune-related diseases
- PMID: 37261359
- PMCID: PMC10228652
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1163633
The role of PD-1 signaling in health and immune-related diseases
Abstract
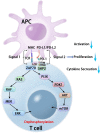
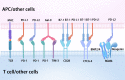
Programmed cell death 1 receptor (PD-1) and its ligands constitute an inhibitory pathway to mediate the mechanism of immune tolerance and provide immune homeostasis. Significantly, the binding partners of PD-1 and its associated ligands are diverse, which facilitates immunosuppression in cooperation with other immune checkpoint proteins. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated the important immunosuppressive role of the PD-1 axis in the tumor microenvironment and in autoimmune diseases. In addition, PD-1 blockades have been approved to treat various cancers, including solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Here, we provide a comprehensive review of the PD-1 pathway, focusing on the structure and expression of PD-1, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), and programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PD-L2); the diverse biological functions of PD-1 signaling in health and immune-related diseases (including tumor immunity, autoimmunity, infectious immunity, transplantation immunity, allergy and immune privilege); and immune-related adverse events related to PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; immune checkpoint proteins; immune tolerance; immunotherapy; programmed cell death 1 receptor; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Zhu, Shen, Xu, Tang, Cui, Jiang, Dai, Chen, Lin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

