Two-action task, testing imitative social learning in kea (Nestor notabilis)
- PMID: 37261570
- PMCID: PMC10345029
- DOI: 10.1007/s10071-023-01788-9
Two-action task, testing imitative social learning in kea (Nestor notabilis)
Erratum in
-
Correction: Two-action task, testing imitative social learning in kea (Nestor notabilis).Anim Cogn. 2023 Jul;26(4):1409. doi: 10.1007/s10071-023-01803-z. Anim Cogn. 2023. PMID: 37340229 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Social learning is an adaptive way of dealing with the complexity of life as it reduces the risk of trial-and-error learning. Depending on the type of information acquired, and associations formed, several mechanisms within the larger taxonomy of social learning can be distinguished. Imitation is one such process within this larger taxonomy, it is considered cognitively demanding and is associated with high-fidelity response matching. The present study reproduced a 2002 study conducted by Heyes and Saggerson, which successfully illustrated motor imitation in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). In our study, eighteen kea (Nestor notabilis) that observed a trained demonstrator remove a stopper from a test box (1) took less time from hopping on the box to feeding (response duration) in session one and (2) were faster in making a vertical removal response on the stopper once they hopped on the box (removal latency) in session one than non-observing control group individuals. In contrast to the budgerigars (Heyes and Saggerson, Ani Behav. 64:851-859, 2002) the present study could not find evidence of motor imitation in kea. The results do illustrate, however, that there were strong social effects on exploration rates indicating motivational and attentional shifts. Furthermore, the results may suggest a propensity toward emulation in contrast to motor imitation or alternatively selectivity in the application of imitation.
Keywords: Emulation; Imitation; Kea; Nestor norabilis; Social learning; Two-action task.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is not conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


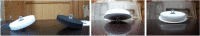
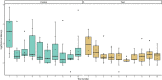

Similar articles
-
Kea, bird of versatility. Kea parrots (Nestor notabilis) show high behavioural flexibility in solving a demonstrated sequence task.J Ornithol. 2024;165(1):49-55. doi: 10.1007/s10336-023-02127-y. Epub 2023 Dec 16. J Ornithol. 2024. PMID: 38225935 Free PMC article.
-
Budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus) copy virtual demonstrators in a two-action test.J Comp Psychol. 2003 Dec;117(4):363-70. doi: 10.1037/0735-7036.117.4.363. J Comp Psychol. 2003. PMID: 14717637
-
Automatic imitation in budgerigars.Proc Biol Sci. 2008 Nov 22;275(1651):2547-53. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2008.0566. Proc Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18664439 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on observational learning in animals.J Comp Psychol. 2012 May;126(2):114-28. doi: 10.1037/a0025381. Epub 2011 Sep 5. J Comp Psychol. 2012. PMID: 21895354 Review.
-
Imitation and local enhancement: detrimental effects of consensus definitions on analyses of social learning in animals.Behav Processes. 2013 Nov;100:123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2013.07.026. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Behav Processes. 2013. PMID: 23954830 Review.
Cited by
-
Feathered Lectures-Evidence of Perceptual Factors on Social Learning in Kea Parrots (Nestor notabilis).Animals (Basel). 2024 May 31;14(11):1651. doi: 10.3390/ani14111651. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891698 Free PMC article.
-
Social learning in dogs from an ecologically valid perspective.Biol Futur. 2025 Jun;76(2):233-248. doi: 10.1007/s42977-025-00271-5. Epub 2025 Jul 25. Biol Futur. 2025. PMID: 40711725 Review.
-
Kea, bird of versatility. Kea parrots (Nestor notabilis) show high behavioural flexibility in solving a demonstrated sequence task.J Ornithol. 2024;165(1):49-55. doi: 10.1007/s10336-023-02127-y. Epub 2023 Dec 16. J Ornithol. 2024. PMID: 38225935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akins CK, Zentall TR. Imitation in Japanese quail: the role of reinforcement of demonstrator responding. Psychon Bull Rev. 1998;5:694–697. doi: 10.3758/BF03208847. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

