Vascular Inflammation, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 37261651
- PMCID: PMC12258637
- DOI: 10.1007/s11912-023-01426-0
Vascular Inflammation, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
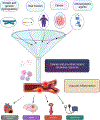
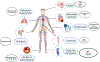
Purpose of review: Cancer and cardiovascular disease are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the USA. Cancer and cardiovascular disease have inflammatory underpinnings that have been associated with both the development and progression of these disease states.
Recent findings: Inflammatory signaling has been found to be a critical event in both cardiovascular disease and cancer formation and progression. Further, many chemotherapeutic agents potentiate inflammation exacerbating existing cardiovascular disease or leading to its presence. The exact mechanisms of these interactions remain poorly understood. The proinflammatory milieu observed in both cancer and cardiovascular disease likely plays an important role in the development and potentiation of both conditions. Further evaluation of this relationship will be critical in the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic modalities.
Keywords: Cardio-oncology; Cardiotoxicity; Endothelial dysfunction; Inflammation.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Johnson CB, Davis MK, Law A, Sulpher J. Shared risk factors for cardiovascular disease and cancer: implications for preventive health and clinical care in oncology patients. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32:900–7. - PubMed
-
- Kamp DW, Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Chronic inflammation and cancer: the role of the mitochondria. Oncology (Williston Park). 2011;25(400–10):13. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83:456S–60S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

