Transforming Growth Factor-β Blockade in Pancreatic Cancer Enhances Sensitivity to Combination Chemotherapy
- PMID: 37263309
- PMCID: PMC10526623
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.038
Transforming Growth Factor-β Blockade in Pancreatic Cancer Enhances Sensitivity to Combination Chemotherapy
Abstract
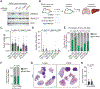
Background & aims: Transforming growth factor-b (TGFb) plays pleiotropic roles in pancreatic cancer, including promoting metastasis, attenuating CD8 T-cell activation, and enhancing myofibroblast differentiation and deposition of extracellular matrix. However, single-agent TGFb inhibition has shown limited efficacy against pancreatic cancer in mice or humans.
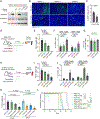
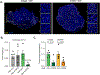
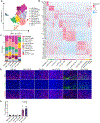
Methods: We evaluated the TGFβ-blocking antibody NIS793 in combination with gemcitabine/nanoparticle (albumin-bound)-paclitaxel or FOLFIRINOX (folinic acid [FOL], 5-fluorouracil [F], irinotecan [IRI] and oxaliplatin [OX]) in orthotopic pancreatic cancer models. Single-cell RNA sequencing and immunofluorescence were used to evaluate changes in tumor cell state and the tumor microenvironment.
Results: Blockade of TGFβ with chemotherapy reduced tumor burden in poorly immunogenic pancreatic cancer, without affecting the metastatic rate of cancer cells. Efficacy of combination therapy was not dependent on CD8 T cells, because response to TGFβ blockade was preserved in CD8-depleted or recombination activating gene 2 (RAG2-/-) mice. TGFβ blockade decreased total α-smooth muscle actin-positive fibroblasts but had minimal effect on fibroblast heterogeneity. Bulk RNA sequencing on tumor cells sorted ex vivo revealed that tumor cells treated with TGFβ blockade adopted a classical lineage consistent with enhanced chemosensitivity, and immunofluorescence for cleaved caspase 3 confirmed that TGFβ blockade increased chemotherapy-induced cell death in vivo.
Conclusions: TGFβ regulates pancreatic cancer cell plasticity between classical and basal cell states. TGFβ blockade in orthotropic models of pancreatic cancer enhances sensitivity to chemotherapy by promoting a classical malignant cell state. This study provides scientific rationale for evaluation of NIS793 with FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine/nanoparticle (albumin-bound) paclitaxel chemotherapy backbone in the clinical setting and supports the concept of manipulating cancer cell plasticity to increase the efficacy of combination therapy regimens.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Immunotherapy; Pancreatic cancer; TGF-β; Tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
SKD received research funding for this project from Novartis Institute for Biomedical Research. VC and MP are employees of Novartis Institute for Biomedical Research. SKD received research funding unrelated to this project from Eli Lilly and Company, Genocea, and Bristol-Myers Squibb and is a founder, science advisory board member (SAB) and equity holder in Kojin. MD has research funding unrelated to this project from Eli Lilly; he has received consulting fees from Genentech, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Partner Therapeutics, SQZ Biotech, AzurRx, Eli Lilly, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Aditum, Foghorn Therapeutics, Palleon, and Moderna; and he is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board for Neoleukin Therapeutics, Veravas, and Cerberus Therapeutics. SR holds equity in Amgen. AJA has consulted for Anji Pharmaceuticals, Arrakis Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Oncorus, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Mirati Therapeutics, Nimbus Therapeutics, Plexium, Revolution Medicines, Reactive Biosciences, Riva Therapeutics, Servier Pharmaceuticals, Syros Pharmaceuticals, Tknife Therapeutics. AJA holds equity in Riva Therapeutics. AJA has research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Deerfield, Inc., Eli Lilly, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, Novo Ventures, Revolution Medicines, and Syros Pharmaceuticals.
Figures


References
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2014;74:2913–21. - PubMed
-
- Hosein AN, Dougan SK, Aguirre AJ, et al. Translational advances in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma therapy. Nat Cancer 2022;3:272–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

