Recombinant ferritins for multimodal nanomedicine
- PMID: 37263586
- PMCID: PMC10236959
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2219868
Recombinant ferritins for multimodal nanomedicine
Abstract
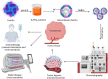
In all living organisms, ferritins are a group of proteins important for maintaining iron homeostasis. Increasing amount of studies has shown that recombinant ferritins can be widely used in multimodal nanomedicine, especially for anticancer treatment and vaccination. Recombinant particles prepared by fusing viral proteins and ferritin subunits produce a better immune response and higher antibody titres. Moreover, actively-targeted ferritin nanoparticles can recognise receptors and deliver natural or chemical drugs specifically to the tumour tissue. In addition, ferritin-linked or loaded with contrast agents or fluorescent dyes can be used as multimodal particles useful cancer theranostics. In this review, we fully summarised the unitisation of recombinant ferritins in multimodal nanomedicine. The research progress of using recombinant ferritins as nanovaccines, nanozymes, and bioengineered nanocarriers for targeted therapy and bioimaging is emphasised.
Keywords: Ferritin; nanocarrier; nanovaccine; nanozymes; recombinant protein.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures






References
-
- Zhang N, Yu XQ, Xie JX, Xu HM.. New insights into the role of ferritin in iron homeostasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(6):2812–2823. - PubMed
-
- Zang JC, Chen H, Zhao GH, Wang FD, Ren FZ.. Ferritin cage for encapsulation and delivery of bioactive nutrients: from structure, property to applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017;57(17):3673–3683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
