Association of dysanapsis with mortality among older adults
- PMID: 37263750
- PMCID: PMC10580540
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00551-2023
Association of dysanapsis with mortality among older adults
Abstract
Dysanapsis – an anthropometric mismatch between airway tree calibre and lung size that is common in the general population – is strongly associated with all-cause mortality and increases susceptibility to tobacco smoking-related diseases
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: C. Sack reports grants from NIEHS K23ES030725-04, outside the submitted work. E.A. Hoffman reports support for the present manuscript from NIH; E.A. Hoffman also reports that he is founder and shareholder of VIDA Diagnostics, and an unpaid member of Photon Counting CT advisory board for Siemens Healthineers, outside the submitted work. N.B. Allen reports support for the present manuscript from NIH/NHLBI; N.B. Allen also reports grants from NIH/NHLBI, outside the submitted work. J. Guo reports support for the present manuscript from National Institutes of Health; J. Guo also reports being a shareholder of VIDA Diagnostics, outside the submitted work. E.D. Michos reports advisory board participation with AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Pfizer, outside the submitted work. S.J. Shea reports support for the present manuscript from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. R.G. Barr reports support for the present manuscript from NIH, COPD Foundation and Foundation for the NIH; R.G. Barr also reports grants from American Lung Association, and advisory board participation with COPD Foundation, outside the submitted work. B.M. Smith reports support for the present manuscript from NIH, Canadian Lung Association, CIHR and Quebec Health Research Fund. All other authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
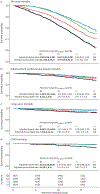
References
-
- Green M, Mead J, Turner JM. Variability of maximum expiratory flow-volume curves. J Appl Physiol 1974; 37: 67–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130506/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 ES030725/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL130627/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 ES034064/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
